2012 Amateur Extra pool
128 / 700 questions need explanations
All explanations are written and maintained by ordinary users like you! Please help us finish the explanations in this pool.
Which of the following conditions apply when transmitting spread spectrum emission?
-
A station transmitting SS emission must not cause harmful interference to other stations employing other authorized emissions (0% chose this)
-
The transmitting station must be in an area regulated by the FCC or in a country that permits SS emissions (0% chose this)
-
The transmission must not be used to obscure the meaning of any communication (0% chose this)
-
All of these choices are correct (0% chose this)
Which of the following best describes one of the standards that must be met by an external RF power amplifier if it is to qualify for a grant of FCC certification?
-
It must produce full legal output when driven by not more than 5 watts of mean RF input power (0% chose this)
-
It must be capable of external RF switching between its input and output networks (0% chose this)
-
It must exhibit a gain of 0 dB or less over its full output range (0% chose this)
-
It must satisfy the FCC's spurious emission standards when operated at the lesser of 1500 watts, or its full output power (0% chose this)
Which of the following types of signals can be relayed through a linear transponder?
-
FM and CW (0% chose this)
-
SSB and SSTV (0% chose this)
-
PSK and Packet (0% chose this)
-
All of these choices are correct (0% chose this)
Why may the received signal from an amateur satellite exhibit a rapidly repeating fading effect?
-
Because the satellite is spinning (0% chose this)
-
Because of ionospheric absorption (0% chose this)
-
Because of the satellite's low orbital altitude (0% chose this)
-
Because of the Doppler Effect (0% chose this)
How is an interlaced scanning pattern generated in a fast-scan (NTSC) television system?
-
By scanning two fields simultaneously (0% chose this)
-
By scanning each field from bottom to top (0% chose this)
-
By scanning lines from left to right in one field and right to left in the next (0% chose this)
-
By scanning odd numbered lines in one field and even numbered ones in the next (0% chose this)
What is blanking in a video signal?
-
Synchronization of the horizontal and vertical sync pulses (0% chose this)
-
Turning off the scanning beam while it is traveling from right to left or from bottom to top (0% chose this)
-
Turning off the scanning beam at the conclusion of a transmission (0% chose this)
-
Transmitting a black and white test pattern (0% chose this)
Which of the following is a common method of transmitting accompanying audio with amateur fast-scan television?
-
Frequency-modulated sub-carrier (0% chose this)
-
A separate VHF or UHF audio link (0% chose this)
-
Frequency modulation of the video carrier (0% chose this)
-
All of these choices are correct (0% chose this)
What hardware, other than a receiver with SSB capability and a suitable computer, is needed to decode SSTV using Digital Radio Mondiale (DRM)?
-
A special IF converter (0% chose this)
-
A special front end limiter (0% chose this)
-
A special notch filter to remove synchronization pulses (0% chose this)
-
No other hardware is needed (0% chose this)
What aspect of an amateur slow-scan television signal encodes the brightness of the picture?
-
Tone frequency (0% chose this)
-
Tone amplitude (0% chose this)
-
Sync amplitude (0% chose this)
-
Sync frequency (0% chose this)
What special operating frequency restrictions are imposed on slow scan TV transmissions?
-
None; they are allowed on all amateur frequencies (0% chose this)
-
They are restricted to 7.245 MHz, 14.245 MHz, 21.345, MHz, and 28.945 MHz (0% chose this)
-
They are restricted to phone band segments and their bandwidth can be no greater than that of a voice signal of the same modulation type (0% chose this)
-
They are not permitted above 54 MHz (0% chose this)
During a VHF/UHF contest, in which band segment would you expect to find the highest level of activity?
-
At the top of each band, usually in a segment reserved for contests (0% chose this)
-
In the middle of each band, usually on the national calling frequency (0% chose this)
-
In the weak signal segment of the band, with most of the activity near the calling frequency (0% chose this)
-
In the middle of the band, usually 25 kHz above the national calling frequency (0% chose this)
How does the spread-spectrum technique of frequency hopping work?
-
If interference is detected by the receiver it will signal the transmitter to change frequencies (0% chose this)
-
If interference is detected by the receiver it will signal the transmitter to wait until the frequency is clear (0% chose this)
-
A pseudo-random binary bit stream is used to shift the phase of an RF carrier very rapidly in a particular sequence (0% chose this)
-
The frequency of the transmitted signal is changed very rapidly according to a particular sequence also used by the receiving station (0% chose this)
Which of the following techniques is normally used by low Earth orbiting digital satellites to relay messages around the world?
-
Digipeating (0% chose this)
-
Store-and-forward (0% chose this)
-
Multi-satellite relaying (0% chose this)
-
Node hopping (0% chose this)
What is indicated when one of the ellipses in an FSK crossed-ellipse display suddenly disappears?
-
Selective fading has occurred (0% chose this)
-
One of the signal filters has saturated (0% chose this)
-
The receiver has drifted 5 kHz from the desired receive frequency (0% chose this)
-
The mark and space signal have been inverted (0% chose this)
Which of the following is a good technique for making meteor-scatter contacts?
-
15 second timed transmission sequences with stations alternating based on location (0% chose this)
-
Use of high speed CW or digital modes (0% chose this)
-
Short transmission with rapidly repeated call signs and signal reports (0% chose this)
-
All of these choices are correct (0% chose this)
Which amateur bands typically support long-path propagation?
-
160 to 40 meters (0% chose this)
-
30 to 10 meters (0% chose this)
-
160 to 10 meters (0% chose this)
-
6 meters to 2 meters (0% chose this)
Which of the following effects does Aurora activity have on radio communications?
-
SSB signals are raspy (0% chose this)
-
Signals propagating through the Aurora are fluttery (0% chose this)
-
CW signals appear to be modulated by white noise (0% chose this)
-
All of these choices are correct (0% chose this)
Which of the following test instruments is used to display intermodulation distortion products in an SSB transmission?
-
A wattmeter (0% chose this)
-
A spectrum analyzer (0% chose this)
-
A logic analyzer (0% chose this)
-
A time-domain reflectometer (0% chose this)
Which of the following could be determined with a spectrum analyzer?
-
The degree of isolation between the input and output ports of a 2 meter duplexer (0% chose this)
-
Whether a crystal is operating on its fundamental or overtone frequency (0% chose this)
-
The spectral output of a transmitter (0% chose this)
-
All of these choices are correct (0% chose this)
Which of the following describes a good method for measuring the intermodulation distortion of your own PSK signal?
-
Transmit into a dummy load, receive the signal on a second receiver, and feed the audio into the sound card of a computer running an appropriate PSK program (0% chose this)
-
Multiply the ALC level on the transmitter during a normal transmission by the average power output (0% chose this)
-
Use an RF voltmeter coupled to the transmitter output using appropriate isolation to prevent damage to the meter (0% chose this)
-
All of these choices are correct (0% chose this)
What is indicated if the current reading on an RF ammeter placed in series with the antenna feed line of a transmitter increases as the transmitter is tuned to resonance?
-
There is possibly a short to ground in the feed line (0% chose this)
-
The transmitter is not properly neutralized (0% chose this)
-
There is an impedance mismatch between the antenna and feed line (0% chose this)
-
There is more power going into the antenna (0% chose this)
What is the definition of the noise figure of a receiver?
-
The ratio of atmospheric noise to phase noise (0% chose this)
-
The noise bandwidth in Hertz compared to the theoretical bandwidth of a resistive network (0% chose this)
-
The ratio of thermal noise to atmospheric noise (0% chose this)
-
The ratio in dB of the noise generated by the receiver compared to the theoretical minimum noise (0% chose this)
Which of the following describes the most significant effect of an off-frequency signal when it is causing cross-modulation interference to a desired signal?
-
A large increase in background noise (0% chose this)
-
A reduction in apparent signal strength (0% chose this)
-
The desired signal can no longer be heard (0% chose this)
-
The off-frequency unwanted signal is heard in addition to the desired signal (0% chose this)
What is the purpose of the preselector in a communications receiver?
-
To store often-used frequencies (0% chose this)
-
To provide a range of AGC time constants (0% chose this)
-
To increase rejection of unwanted signals (0% chose this)
-
To allow selection of the optimum RF amplifier device (0% chose this)
What is the term for the reduction in receiver sensitivity caused by a strong signal near the received frequency?
-
Desensitization (0% chose this)
-
Quieting (0% chose this)
-
Cross-modulation interference (0% chose this)
-
Squelch gain rollback (0% chose this)
How can conducted and radiated noise caused by an automobile alternator be suppressed?
-
By installing filter capacitors in series with the DC power lead and by installing a blocking capacitor in the field lead (0% chose this)
-
By installing a noise suppression resistor and a blocking capacitor in both leads (0% chose this)
-
By installing a high-pass filter in series with the radio's power lead and a low-pass filter in parallel with the field lead (0% chose this)
-
By connecting the radio's power leads directly to the battery and by installing coaxial capacitors in line with the alternator leads (0% chose this)
Which of the following is the most likely cause if you are hearing combinations of local AM broadcast signals within one or more of the MF or HF ham bands?
-
The broadcast station is transmitting an over-modulated signal (0% chose this)
-
Nearby corroded metal joints are mixing and re-radiating the broadcast signals (0% chose this)
-
You are receiving sky wave signals from a distant station (0% chose this)
-
Your station receiver IF amplifier stage is defective (0% chose this)
What is one disadvantage of using some types of automatic DSP notch-filters when attempting to copy CW signals?
-
The DSP filter can remove the desired signal at the same time as it removes interfering signals (0% chose this)
-
Any nearby signal passing through the DSP system will overwhelm the desired signal (0% chose this)
-
Received CW signals will appear to be modulated at the DSP clock frequency (0% chose this)
-
Ringing in the DSP filter will completely remove the spaces between the CW characters (0% chose this)
What do the two numbers represent that are used to define a point on a graph using rectangular coordinates?
-
The magnitude and phase of the point (0% chose this)
-
The sine and cosine values (0% chose this)
-
The coordinate values along the horizontal and vertical axes (0% chose this)
-
The tangent and cotangent values (0% chose this)
What coordinate system is often used to display the resistive, inductive, and/or capacitive reactance components of an impedance?
-
Maidenhead grid (0% chose this)
-
Faraday grid (0% chose this)
-
Elliptical coordinates (0% chose this)
-
Rectangular coordinates (0% chose this)
What type of energy is stored in an electromagnetic or electrostatic field?
-
Electromechanical energy (0% chose this)
-
Potential energy (0% chose this)
-
Thermodynamic energy (0% chose this)
-
Kinetic energy (0% chose this)
What happens to reactive power in an AC circuit that has both ideal inductors and ideal capacitors?
-
It is dissipated as heat in the circuit (0% chose this)
-
It is repeatedly exchanged between the associated magnetic and electric fields, but is not dissipated (0% chose this)
-
It is dissipated as kinetic energy in the circuit (0% chose this)
-
It is dissipated in the formation of inductive and capacitive fields (0% chose this)
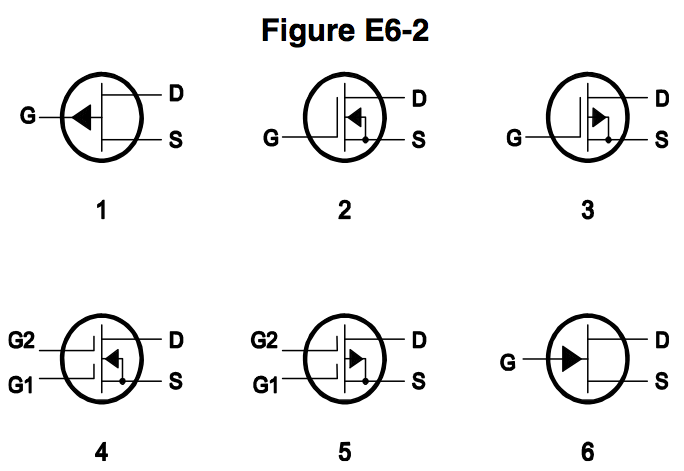
In Figure E6-2, what is the schematic symbol for an N-channel dual-gate MOSFET?
-
2 (0% chose this)
-
4 (0% chose this)
-
5 (0% chose this)
-
6 (0% chose this)
Why do many MOSFET devices have internally connected Zener diodes on the gates?
-
To provide a voltage reference for the correct amount of reverse-bias gate voltage (0% chose this)
-
To protect the substrate from excessive voltages (0% chose this)
-
To keep the gate voltage within specifications and prevent the device from overheating (0% chose this)
-
To reduce the chance of the gate insulation being punctured by static discharges or excessive voltages (0% chose this)
What is the failure mechanism when a junction diode fails due to excessive current?
-
Excessive inverse voltage (0% chose this)
-
Excessive junction temperature (0% chose this)
-
Insufficient forward voltage (0% chose this)
-
Charge carrier depletion (0% chose this)
Which of the following describes a type of semiconductor diode?
-
Metal-semiconductor junction (0% chose this)
-
Electrolytic rectifier (0% chose this)
-
CMOS-field effect (0% chose this)
-
Thermionic emission diode (0% chose this)
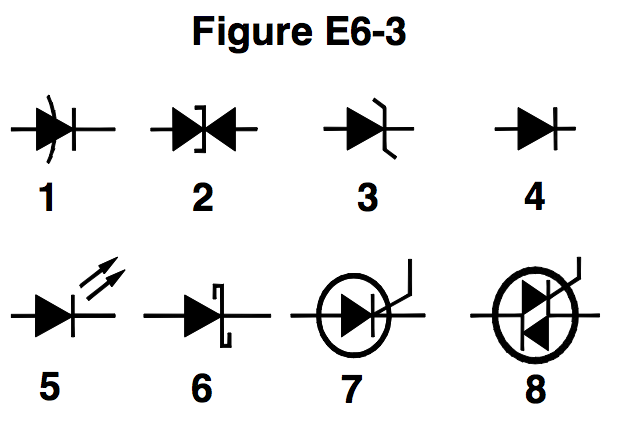
In Figure E6-3, what is the schematic symbol for a light-emitting diode?
-
1 (0% chose this)
-
5 (0% chose this)
-
6 (0% chose this)
-
7 (0% chose this)
What is the recommended power supply voltage for TTL series integrated circuits?
-
12 volts (0% chose this)
-
1.5 volts (0% chose this)
-
5 volts (0% chose this)
-
13.6 volts (0% chose this)
What logic state do the inputs of a TTL device assume if they are left open?
-
A logic-high state (0% chose this)
-
A logic-low state (0% chose this)
-
The device becomes randomized and will not provide consistent high or low-logic states (0% chose this)
-
Open inputs on a TTL device are ignored (0% chose this)
Which of the following describes tri-state logic?
-
Logic devices with 0, 1, and high impedance output states (0% chose this)
-
Logic devices that utilize ternary math (0% chose this)
-
Low power logic devices designed to operate at 3 volts (0% chose this)
-
Proprietary logic devices manufactured by Tri-State Devices (0% chose this)
Which of the following is an advantage of CMOS logic devices over TTL devices?
-
Differential output capability (0% chose this)
-
Lower distortion (0% chose this)
-
Immune to damage from static discharge (0% chose this)
-
Lower power consumption (0% chose this)

In Figure E6-5, what is the schematic symbol for a NAND gate?
-
1 (0% chose this)
-
2 (0% chose this)
-
3 (0% chose this)
-
4 (0% chose this)
What is a crystal lattice filter?
-
A power supply filter made with interlaced quartz crystals (0% chose this)
-
An audio filter made with four quartz crystals that resonate at 1-kHz intervals (0% chose this)
-
A filter with wide bandwidth and shallow skirts made using quartz crystals (0% chose this)
-
A filter with narrow bandwidth and steep skirts made using quartz crystals (0% chose this)
Which of the following factors has the greatest effect in helping determine the bandwidth and response shape of a crystal ladder filter?
-
The relative frequencies of the individual crystals (0% chose this)
-
The DC voltage applied to the quartz crystal (0% chose this)
-
The gain of the RF stage preceding the filter (0% chose this)
-
The amplitude of the signals passing through the filter (0% chose this)
What characteristics of the MMIC make it a popular choice for VHF through microwave circuits?
-
The ability to retrieve information from a single signal even in the presence of other strong signals. (0% chose this)
-
Plate current that is controlled by a control grid (0% chose this)
-
Nearly infinite gain, very high input impedance, and very low output impedance (0% chose this)
-
Controlled gain, low noise figure, and constant input and output impedance over the specified frequency range (0% chose this)
How is power-supply voltage normally furnished to the most common type of monolithic microwave integrated circuit (MMIC)?
-
Through a resistor and/or RF choke connected to the amplifier output lead (0% chose this)
-
MMICs require no operating bias (0% chose this)
-
Through a capacitor and RF choke connected to the amplifier input lead (0% chose this)
-
Directly to the bias-voltage (VCC IN) lead (0% chose this)
What is photoconductivity?
-
The conversion of photon energy to electromotive energy (0% chose this)
-
The increased conductivity of an illuminated semiconductor (0% chose this)
-
The conversion of electromotive energy to photon energy (0% chose this)
-
The decreased conductivity of an illuminated semiconductor (0% chose this)
Which of these materials is affected the most by photoconductivity?
-
A crystalline semiconductor (0% chose this)
-
An ordinary metal (0% chose this)
-
A heavy metal (0% chose this)
-
A liquid semiconductor (0% chose this)
What absorbs the energy from light falling on a photovoltaic cell?
-
Protons (0% chose this)
-
Photons (0% chose this)
-
Electrons (0% chose this)
-
Holes (0% chose this)
How can an RF power amplifier be neutralized?
-
By increasing the driving power (0% chose this)
-
By reducing the driving power (0% chose this)
-
By feeding a 180-degree out-of-phase portion of the output back to the input (0% chose this)
-
By feeding an in-phase component of the output back to the input (0% chose this)
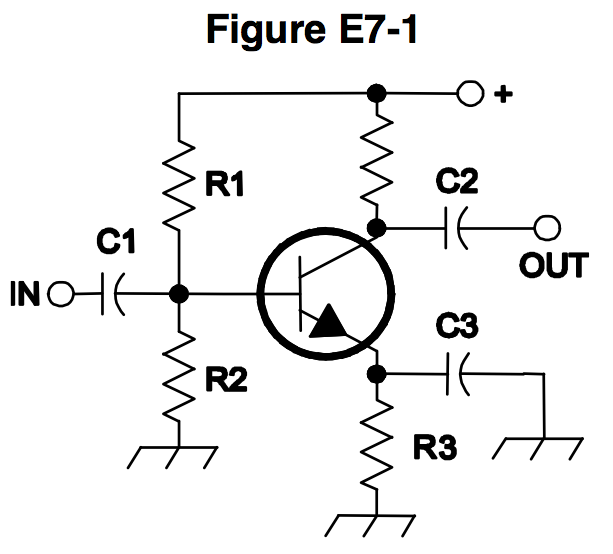
In Figure E7-1, what is the purpose of R1 and R2?
-
Load resistors (0% chose this)
-
Fixed bias (0% chose this)
-
Self bias (0% chose this)
-
Feedback (0% chose this)
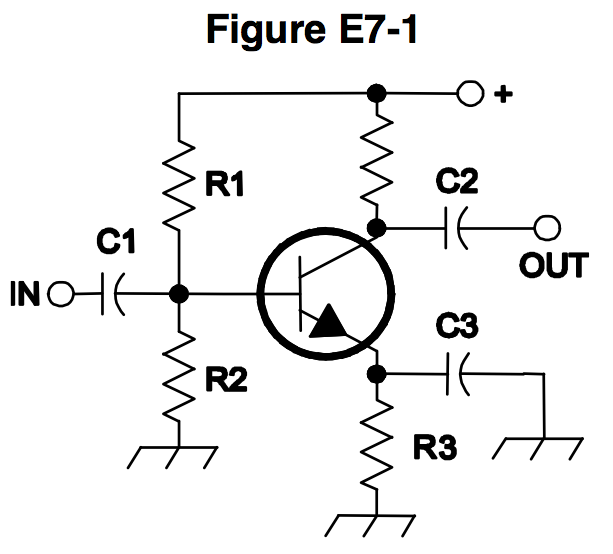
In Figure E7-1, what is the purpose of R3?
-
Fixed bias (0% chose this)
-
Emitter bypass (0% chose this)
-
Output load resistor (0% chose this)
-
Self bias (0% chose this)
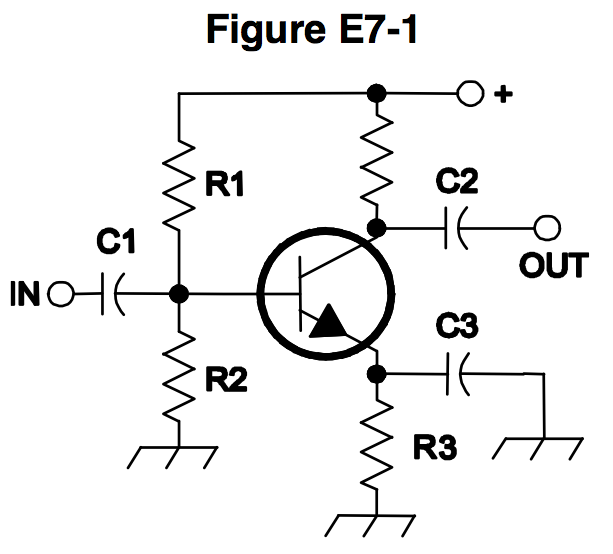
What type of circuit is shown in Figure E7-1?
-
Switching voltage regulator (0% chose this)
-
Linear voltage regulator (0% chose this)
-
Common emitter amplifier (0% chose this)
-
Emitter follower amplifier (0% chose this)

In Figure E7-2, what is the purpose of C2?
-
Output coupling (0% chose this)
-
Emitter bypass (0% chose this)
-
Input coupling (0% chose this)
-
Hum filtering (0% chose this)
Why are third-order intermodulation distortion products of particular concern in linear power amplifiers?
-
Because they are relatively close in frequency to the desired signal (0% chose this)
-
Because they are relatively far in frequency from the desired signal (0% chose this)
-
Because they invert the sidebands causing distortion (0% chose this)
-
Because they maintain the sidebands, thus causing multiple duplicate signals (0% chose this)
What advantage does a Pi-L-network have over a Pi-network for impedance matching between the final amplifier of a vacuum-tube transmitter and an antenna?
-
Greater harmonic suppression (0% chose this)
-
Higher efficiency (0% chose this)
-
Lower losses (0% chose this)
-
Greater transformation range (0% chose this)
What is one advantage of a Pi matching network over an L matching network consisting of a single inductor and a single capacitor?
-
The Q of Pi networks can be varied depending on the component values chosen (0% chose this)
-
L networks cannot perform impedance transformation (0% chose this)
-
Pi networks have fewer components (0% chose this)
-
Pi networks are designed for balanced input and output (0% chose this)
Which of these modes is most affected by non-linear phase response in a receiver IF filter?
-
Meteor Scatter (0% chose this)
-
Single-Sideband voice (0% chose this)
-
Digital (0% chose this)
-
Video (0% chose this)
What is one characteristic of a switching electronic voltage regulator?
-
The resistance of a control element is varied in direct proportion to the line voltage or load current (0% chose this)
-
It is generally less efficient than a linear regulator (0% chose this)
-
The control device's duty cycle is controlled to produce a constant average output voltage (0% chose this)
-
It gives a ramp voltage at its output (0% chose this)
Which of the following types of linear voltage regulator usually make the most efficient use of the primary power source?
-
A series current source (0% chose this)
-
A series regulator (0% chose this)
-
A shunt regulator (0% chose this)
-
A shunt current source (0% chose this)

What is the purpose of Q1 in the circuit shown in Figure E7-3?
-
It provides negative feedback to improve regulation (0% chose this)
-
It provides a constant load for the voltage source (0% chose this)
-
It increases the current-handling capability of the regulator (0% chose this)
-
It provides D1 with current (0% chose this)

What type of circuit is shown in Figure E7-3?
-
Switching voltage regulator (0% chose this)
-
Grounded emitter amplifier (0% chose this)
-
Linear voltage regulator (0% chose this)
-
Emitter follower (0% chose this)

What is the purpose of C1 in the circuit shown in Figure E7-3?
-
It resonates at the ripple frequency (0% chose this)
-
It provides fixed bias for Q1 (0% chose this)
-
It decouples the output (0% chose this)
-
It filters the supply voltage (0% chose this)

What is the purpose of C3 in the circuit shown in Figure E7-3?
-
It prevents self-oscillation (0% chose this)
-
It provides brute force filtering of the output (0% chose this)
-
It provides fixed bias for Q1 (0% chose this)
-
It clips the peaks of the ripple (0% chose this)

What is the purpose of R1 in the circuit shown in Figure E7-3?
-
It provides a constant load to the voltage source (0% chose this)
-
It couples hum to D1 (0% chose this)
-
It supplies current to D1 (0% chose this)
-
It bypasses hum around D1 (0% chose this)

What is the purpose of R2 in the circuit shown in Figure E7-3?
-
It provides fixed bias for Q1 (0% chose this)
-
It provides fixed bias for D1 (0% chose this)
-
It decouples hum from D1 (0% chose this)
-
It provides a constant minimum load for Q1 (0% chose this)
What is the purpose of a "step-start" circuit in a high-voltage power supply?
-
To provide a dual-voltage output for reduced power applications (0% chose this)
-
To compensate for variations of the incoming line voltage (0% chose this)
-
To allow for remote control of the power supply (0% chose this)
-
To allow the filter capacitors to charge gradually (0% chose this)
When several electrolytic filter capacitors are connected in series to increase the operating voltage of a power supply filter circuit, why should resistors be connected across each capacitor?
-
To equalize, as much as possible, the voltage drop across each capacitor (0% chose this)
-
To provide a safety bleeder to discharge the capacitors when the supply is off (0% chose this)
-
To provide a minimum load current to reduce voltage excursions at light loads (0% chose this)
-
All of these choices are correct (0% chose this)
Which of the following can be used to generate FM phone emissions?
-
A balanced modulator on the audio amplifier (0% chose this)
-
A reactance modulator on the oscillator (0% chose this)
-
A reactance modulator on the final amplifier (0% chose this)
-
A balanced modulator on the oscillator (0% chose this)
How does an analog phase modulator function?
-
By varying the tuning of a microphone preamplifier to produce PM signals (0% chose this)
-
By varying the tuning of an amplifier tank circuit to produce AM signals (0% chose this)
-
By varying the tuning of an amplifier tank circuit to produce PM signals (0% chose this)
-
By varying the tuning of a microphone preamplifier to produce AM signals (0% chose this)
What is one way a single-sideband phone signal can be generated?
-
By using a balanced modulator followed by a filter (0% chose this)
-
By using a reactance modulator followed by a mixer (0% chose this)
-
By using a loop modulator followed by a mixer (0% chose this)
-
By driving a product detector with a DSB signal (0% chose this)
What are the principal frequencies that appear at the output of a mixer circuit?
-
Two and four times the original frequency (0% chose this)
-
The sum, difference and square root of the input frequencies (0% chose this)
-
The two input frequencies along with their sum and difference frequencies (0% chose this)
-
1.414 and 0.707 times the input frequency (0% chose this)
What occurs when an excessive amount of signal energy reaches a mixer circuit?
-
Spurious mixer products are generated (0% chose this)
-
Mixer blanking occurs (0% chose this)
-
Automatic limiting occurs (0% chose this)
-
A beat frequency is generated (0% chose this)
Which of the following types of detector is well suited for demodulating SSB signals?
-
Discriminator (0% chose this)
-
Phase detector (0% chose this)
-
Product detector (0% chose this)
-
Phase comparator (0% chose this)
What is the purpose of a frequency counter?
-
To provide a digital representation of the frequency of a signal (0% chose this)
-
To generate a series of reference signals at known frequency intervals (0% chose this)
-
To display all frequency components of a transmitted signal (0% chose this)
-
To provide a signal source at a very accurate frequency (0% chose this)
What is an advantage of a period-measuring frequency counter over a direct-count type?
-
It can run on battery power for remote measurements (0% chose this)
-
It does not require an expensive high-precision time base (0% chose this)
-
It provides improved resolution of low-frequency signals within a comparable time period (0% chose this)
-
It can directly measure the modulation index of an FM transmitter (0% chose this)
What primarily determines the gain and frequency characteristics of an op-amp RC active filter?
-
The values of capacitors and resistors built into the op-amp (0% chose this)
-
The values of capacitors and resistors external to the op-amp (0% chose this)
-
The input voltage and frequency of the op-amp's DC power supply (0% chose this)
-
The output voltage and smoothness of the op-amp's DC power supply (0% chose this)
What is the typical input impedance of an integrated circuit op-amp?
-
100 ohms (0% chose this)
-
1000 ohms (0% chose this)
-
Very low (0% chose this)
-
Very high (0% chose this)
What condition must exist for a circuit to oscillate?
-
It must have at least two stages (0% chose this)
-
It must be neutralized (0% chose this)
-
It must have positive feedback with a gain greater than 1 (0% chose this)
-
It must have negative feedback sufficient to cancel the input signal (0% chose this)
What type of frequency synthesizer circuit uses a phase accumulator, lookup table, digital to analog converter and a low-pass anti-alias filter?
-
A direct digital synthesizer (0% chose this)
-
A hybrid synthesizer (0% chose this)
-
A phase locked loop synthesizer (0% chose this)
-
A diode-switching matrix synthesizer (0% chose this)
What information is contained in the lookup table of a direct digital frequency synthesizer?
-
The phase relationship between a reference oscillator and the output waveform (0% chose this)
-
The amplitude values that represent a sine-wave output (0% chose this)
-
The phase relationship between a voltage-controlled oscillator and the output waveform (0% chose this)
-
The synthesizer frequency limits and frequency values stored in the radio memories (0% chose this)
Which of the following is a principal component of a direct digital synthesizer (DDS)?
-
Phase splitter (0% chose this)
-
Hex inverter (0% chose this)
-
Chroma demodulator (0% chose this)
-
Phase accumulator (0% chose this)
What is the capture range of a phase-locked loop circuit?
-
The frequency range over which the circuit can lock (0% chose this)
-
The voltage range over which the circuit can lock (0% chose this)
-
The input impedance range over which the circuit can lock (0% chose this)
-
The range of time it takes the circuit to lock (0% chose this)
Which of these functions can be performed by a phase-locked loop?
-
Wide-band AF and RF power amplification (0% chose this)
-
Comparison of two digital input signals, digital pulse counter (0% chose this)
-
Photovoltaic conversion, optical coupling (0% chose this)
-
Frequency synthesis, FM demodulation (0% chose this)
What is the approximate ratio of PEP-to-average power in a typical single-sideband phone signal?
-
2.5 to 1 (0% chose this)
-
25 to 1 (0% chose this)
-
1 to 1 (0% chose this)
-
100 to 1 (0% chose this)
What is the period of a wave?
-
The time required to complete one cycle (0% chose this)
-
The number of degrees in one cycle (0% chose this)
-
The number of zero crossings in one cycle (0% chose this)
-
The amplitude of the wave (0% chose this)
What type of waveform is produced by human speech?
-
Sinusoidal (0% chose this)
-
Logarithmic (0% chose this)
-
Irregular (0% chose this)
-
Trapezoidal (0% chose this)
Which of the following is a distinguishing characteristic of a pulse waveform?
-
Regular sinusoidal oscillations (0% chose this)
-
Narrow bursts of energy separated by periods of no signal (0% chose this)
-
A series of tones that vary between two frequencies (0% chose this)
-
A signal that contains three or more discrete tones (0% chose this)
What type of information can be conveyed using digital waveforms?
-
Human speech (0% chose this)
-
Video signals (0% chose this)
-
Data (0% chose this)
-
All of these choices are correct (0% chose this)
What is an advantage of using digital signals instead of analog signals to convey the same information?
-
Less complex circuitry is required for digital signal generation and detection (0% chose this)
-
Digital signals always occupy a narrower bandwidth (0% chose this)
-
Digital signals can be regenerated multiple times without error (0% chose this)
-
All of these choices are correct (0% chose this)
What is the term for the ratio between the frequency deviation of an RF carrier wave, and the modulating frequency of its corresponding FM-phone signal?
-
FM compressibility (0% chose this)
-
Quieting index (0% chose this)
-
Percentage of modulation (0% chose this)
-
Modulation index (0% chose this)
How does the modulation index of a phase-modulated emission vary with RF carrier frequency (the modulated frequency)?
-
It increases as the RF carrier frequency increases (0% chose this)
-
It decreases as the RF carrier frequency increases (0% chose this)
-
It varies with the square root of the RF carrier frequency (0% chose this)
-
It does not depend on the RF carrier frequency (0% chose this)
What parameter does the modulating signal vary in a pulse-position modulation system?
-
The number of pulses per second (0% chose this)
-
The amplitude of the pulses (0% chose this)
-
The duration of the pulses (0% chose this)
-
The time at which each pulse occurs (0% chose this)
Which of these methods can be used to combine several separate analog information streams into a single analog radio frequency signal?
-
Frequency shift keying (0% chose this)
-
A diversity combiner (0% chose this)
-
Frequency division multiplexing (0% chose this)
-
Pulse compression (0% chose this)
What technique is used to minimize the bandwidth requirements of a PSK31 signal?
-
Zero-sum character encoding (0% chose this)
-
Reed-Solomon character encoding (0% chose this)
-
Use of sinusoidal data pulses (0% chose this)
-
Use of trapezoidal data pulses (0% chose this)
Which of these techniques causes a digital signal to appear as wide-band noise to a conventional receiver?
-
Spread-spectrum (0% chose this)
-
Independent sideband (0% chose this)
-
Regenerative detection (0% chose this)
-
Exponential addition (0% chose this)
What spread-spectrum communications technique alters the center frequency of a conventional carrier many times per second in accordance with a pseudo-random list of channels?
-
Frequency hopping (0% chose this)
-
Direct sequence (0% chose this)
-
Time-domain frequency modulation (0% chose this)
-
Frequency compandored spread-spectrum (0% chose this)
Which of the following is the easiest voltage amplitude parameter to measure when viewing a pure sine wave signal on an analog oscilloscope?
-
Peak-to-peak voltage (0% chose this)
-
RMS voltage (0% chose this)
-
Average voltage (0% chose this)
-
DC voltage (0% chose this)
What is the advantage of using a peak-reading wattmeter to monitor the output of a SSB phone transmitter?
-
It is easier to determine the correct tuning of the output circuit (0% chose this)
-
It gives a more accurate display of the PEP output when modulation is present (0% chose this)
-
It makes it easier to detect high SWR on the feed line (0% chose this)
-
It can determine if any flat-topping is present during modulation peaks (0% chose this)
What is an electromagnetic wave?
-
Alternating currents in the core of an electromagnet (0% chose this)
-
A wave consisting of two electric fields at right angles to each other (0% chose this)
-
A wave consisting of an electric field and a magnetic field oscillating at right angles to each other (0% chose this)
-
A wave consisting of two magnetic fields at right angles to each other (0% chose this)
Which of the following best describes electromagnetic waves traveling in free space?
-
Electric and magnetic fields become aligned as they travel (0% chose this)
-
The energy propagates through a medium with a high refractive index (0% chose this)
-
The waves are reflected by the ionosphere and return to their source (0% chose this)
-
Changing electric and magnetic fields propagate the energy (0% chose this)
Why would one need to know the feed point impedance of an antenna?
-
To match impedances in order to minimize standing wave ratio on the transmission line (0% chose this)
-
To measure the near-field radiation density from a transmitting antenna (0% chose this)
-
To calculate the front-to-side ratio of the antenna (0% chose this)
-
To calculate the front-to-back ratio of the antenna (0% chose this)
What is meant by antenna gain?
-
The ratio relating the radiated signal strength of an antenna in the direction of maximum radiation to that of a reference antenna (0% chose this)
-
The ratio of the signal in the forward direction to that in the opposite direction (0% chose this)
-
The ratio of the amount of power radiated by an antenna compared to the transmitter output power (0% chose this)
-
The final amplifier gain minus the transmission-line losses, including any phasing lines present (0% chose this)
How is antenna efficiency calculated?
-
(radiation resistance / transmission resistance) x 100% (0% chose this)
-
(radiation resistance / total resistance) x 100% (0% chose this)
-
(total resistance / radiation resistance) x 100% (0% chose this)
-
(effective radiated power / transmitter output) x 100% (0% chose this)
Which of the following choices is a way to improve the efficiency of a ground-mounted quarter-wave vertical antenna?
-
Install a good radial system (0% chose this)
-
Isolate the coax shield from ground (0% chose this)
-
Shorten the radiating element (0% chose this)
-
Reduce the diameter of the radiating element (0% chose this)
What may occur when a directional antenna is operated at different frequencies within the band for which it was designed?
-
Feed point impedance may become negative (0% chose this)
-
The E-field and H-field patterns may reverse (0% chose this)
-
Element spacing limits could be exceeded (0% chose this)
-
The gain may change depending on frequency (0% chose this)
How can the approximate beamwidth in a given plane of a directional antenna be determined?
-
Note the two points where the signal strength of the antenna is 3 dB less than maximum and compute the angular difference (0% chose this)
-
Measure the ratio of the signal strengths of the radiated power lobes from the front and rear of the antenna (0% chose this)
-
Draw two imaginary lines through the ends of the elements and measure the angle between the lines (0% chose this)
-
Measure the ratio of the signal strengths of the radiated power lobes from the front and side of the antenna (0% chose this)
What type of computer program technique is commonly used for modeling antennas?
-
Graphical analysis (0% chose this)
-
Method of Moments (0% chose this)
-
Mutual impedance analysis (0% chose this)
-
Calculus differentiation with respect to physical properties (0% chose this)
What is the principle of a Method of Moments analysis?
-
A wire is modeled as a series of segments, each having a uniform value of current (0% chose this)
-
A wire is modeled as a single sine-wave current generator (0% chose this)
-
A wire is modeled as a series of points, each having a distinct location in space (0% chose this)
-
A wire is modeled as a series of segments, each having a distinct value of voltage across it (0% chose this)
What type of information can be obtained by submitting the details of a proposed new antenna to a modeling program?
-
SWR vs. frequency charts (0% chose this)
-
Polar plots of the far-field elevation and azimuth patterns (0% chose this)
-
Antenna gain (0% chose this)
-
All of these choices are correct (0% chose this)
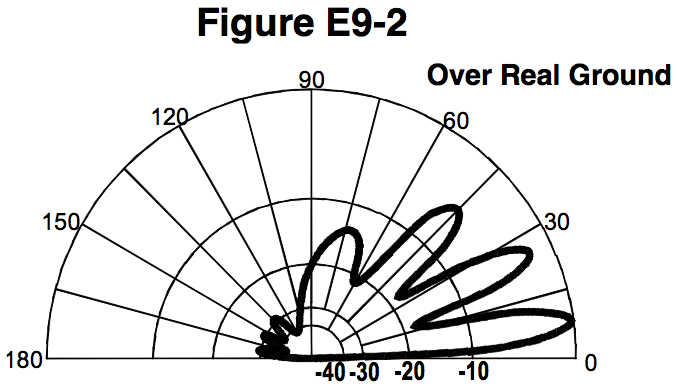
What type of antenna pattern over real ground is shown in Figure E9-2?
-
Elevation (0% chose this)
-
Azimuth (0% chose this)
-
Radiation resistance (0% chose this)
-
Polarization (0% chose this)
What is the main effect of placing a vertical antenna over an imperfect ground?
-
It causes increased SWR (0% chose this)
-
It changes the impedance angle of the matching network (0% chose this)
-
It reduces low-angle radiation (0% chose this)
-
It reduces losses in the radiating portion of the antenna (0% chose this)
How can linearly polarized Yagi antennas be used to produce circular polarization?
-
Stack two Yagis, fed 90 degrees out of phase, to form an array with the respective elements in parallel planes (0% chose this)
-
Stack two Yagis, fed in phase, to form an array with the respective elements in parallel planes (0% chose this)
-
Arrange two Yagis perpendicular to each other with the driven elements at the same point on the boom and fed 90 degrees out of phase (0% chose this)
-
Arrange two Yagis collinear to each other, with the driven elements fed 180 degrees out of phase (0% chose this)
Where should a high-Q loading coil be placed to minimize losses in a shortened vertical antenna?
-
Near the center of the vertical radiator (0% chose this)
-
As low as possible on the vertical radiator (0% chose this)
-
As close to the transmitter as possible (0% chose this)
-
At a voltage node (0% chose this)
What is a disadvantage of using a multiband trapped antenna?
-
It might radiate harmonics (0% chose this)
-
It radiates the harmonics and fundamental equally well (0% chose this)
-
It is too sharply directional at lower frequencies (0% chose this)
-
It must be neutralized (0% chose this)
What is one advantage of using a trapped antenna?
-
It has high directivity in the higher-frequency bands (0% chose this)
-
It has high gain (0% chose this)
-
It minimizes harmonic radiation (0% chose this)
-
It may be used for multiband operation (0% chose this)
Which of these matching systems is an effective method of connecting a 50-ohm coaxial cable feed line to a grounded tower so it can be used as a vertical antenna?
-
Double-bazooka match (0% chose this)
-
Hairpin match (0% chose this)
-
Gamma match (0% chose this)
-
All of these choices are correct (0% chose this)
What is the purpose of a Wilkinson divider?
-
It divides the operating frequency of a transmitter signal so it can be used on a lower frequency band (0% chose this)
-
It is used to feed high-impedance antennas from a low-impedance source (0% chose this)
-
It divides power equally among multiple loads while preventing changes in one load from disturbing power flow to the others (0% chose this)
-
It is used to feed low-impedance loads from a high-impedance source (0% chose this)
What is the typical velocity factor for a coaxial cable with solid polyethylene dielectric?
-
2.70 (0% chose this)
-
0.66 (0% chose this)
-
0.30 (0% chose this)
-
0.10 (0% chose this)
How does ladder line compare to small-diameter coaxial cable such as RG-58 at 50 MHz?
-
Lower loss (0% chose this)
-
Higher SWR (0% chose this)
-
Smaller reflection coefficient (0% chose this)
-
Lower velocity factor (0% chose this)
What impedance does a 1/2-wavelength transmission line present to a generator when the line is open at the far end?
-
Very high impedance (0% chose this)
-
Very low impedance (0% chose this)
-
The same as the characteristic impedance of the line (0% chose this)
-
The same as the output impedance of the generator (0% chose this)
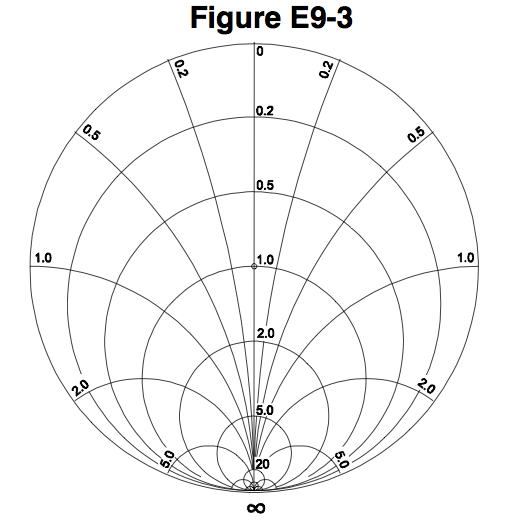
What type of chart is shown in Figure E9-3?
-
Smith chart (0% chose this)
-
Free-space radiation directivity chart (0% chose this)
-
Elevation angle radiation pattern chart (0% chose this)
-
Azimuth angle radiation pattern chart (0% chose this)
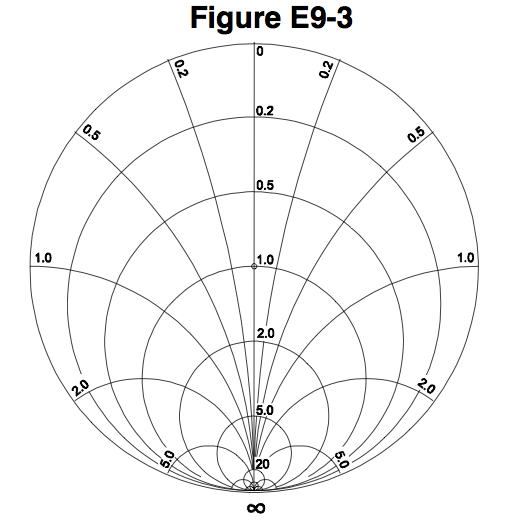
On the Smith chart shown in Figure E9-3, what is the only straight line shown?
-
The reactance axis (0% chose this)
-
The current axis (0% chose this)
-
The voltage axis (0% chose this)
-
The resistance axis (0% chose this)
What do the arcs on a Smith chart represent?
-
Frequency (0% chose this)
-
SWR (0% chose this)
-
Points with constant resistance (0% chose this)
-
Points with constant reactance (0% chose this)
How are the wavelength scales on a Smith chart calibrated?
-
In fractions of transmission line electrical frequency (0% chose this)
-
In fractions of transmission line electrical wavelength (0% chose this)
-
In fractions of antenna electrical wavelength (0% chose this)
-
In fractions of antenna electrical frequency (0% chose this)
What term describes station output, including the transmitter, antenna and everything in between, when considering transmitter power and system gains and losses?
-
Power factor (0% chose this)
-
Half-power bandwidth (0% chose this)
-
Effective radiated power (0% chose this)
-
Apparent power (0% chose this)
Why is it advisable to use an RF attenuator on a receiver being used for direction finding?
-
It narrows the bandwidth of the received signal to improve signal to noise ratio (0% chose this)
-
It compensates for the effects of an isotropic antenna, thereby improving directivity (0% chose this)
-
It reduces loss of received signals caused by antenna pattern nulls, thereby increasing sensitivity (0% chose this)
-
It prevents receiver overload which could make it difficult to determine peaks or nulls (0% chose this)
How can the output voltage of a multi-turn receiving loop antenna be increased?
-
By reducing the permeability of the loop shield (0% chose this)
-
By increasing the number of wire turns in the loop and reducing the area of the loop structure (0% chose this)
-
By winding adjacent turns in opposing directions (0% chose this)
-
By increasing either the number of wire turns in the loop or the area of the loop structure or both (0% chose this)
HamStudy.org™ is copyright 2026 Signal Stuff™, All rights
reserved.
View Privacy Policy | Get help with HamStudy.org™
View Privacy Policy | Get help with HamStudy.org™
