2021 NZART pool
386 / 600 questions need explanations
All explanations are written and maintained by ordinary users like you! Please help us finish the explanations in this pool.
Two basic types of field effect transistors are
-
n-channel and p-channel (50% chose this)
-
NPN and PNP (45% chose this)
-
germanium and silicon (2% chose this)
-
inductive and capacitive (2% chose this)
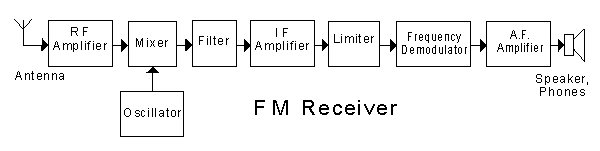
In the block diagram of the receiver shown, an automatic gain control (AGC) circuit would be associated with the
-
Speaker (8% chose this)
-
IF amplifier (55% chose this)
-
RF filter (33% chose this)
-
Oscillator (5% chose this)
The published New Zealand amateur radio bandplans are
-
obligatory for all amateur radio operators to observe (50% chose this)
-
recommended, and all amateur radio operators should follow them (48% chose this)
-
to show where distant stations can be worked (2% chose this)
-
for tests and experimental purposes only (0% chose this)
At the ends of a half-wave dipole the
-
voltage and current are both high (5% chose this)
-
voltage is high and current is low (52% chose this)
-
voltage and current are both low (24% chose this)
-
voltage low and current is high (19% chose this)
To bias a transistor to cut-off, the base must be
-
at the collector potential (31% chose this)
-
at the emitter potential (45% chose this)
-
mid-way between collector and emitter potentials (18% chose this)
-
mid-way between the collector and the supply potentials (6% chose this)
The stage in a superhet receiver with a tuneable input and fixed tuned output is the
-
RF amplifier (9% chose this)
-
mixer stage (53% chose this)
-
IF amplifier (16% chose this)
-
local oscillator (21% chose this)
The following are three digital communication modes
-
DSBSC, PACTOR, NBFM (7% chose this)
-
AGC, FSK, Clover (7% chose this)
-
PSK31, AFC, PSSN (36% chose this)
-
AMTOR, PACTOR, PSK31 (51% chose this)
The capacitor value best suited for smoothing the output of a 12 volt 1 amp DC power supply is
-
100 pF (18% chose this)
-
10 nF (9% chose this)
-
100 nF (31% chose this)
-
10,000 uF (42% chose this)
An amateur radio operator must have current New Zealand postal and email addresses so the Ministry of Business, Innovation, and Employment
-
has a record of the location of each amateur station (40% chose this)
-
can refund overpaid fees (0% chose this)
-
can publish a callsign directory (5% chose this)
-
can send mail to the operator (55% chose this)
A transmitter power amplifier has a gain of 20 dB. The ratio of the output power to the input power is
-
10 (25% chose this)
-
20 (19% chose this)
-
40 (13% chose this)
-
100 (43% chose this)
Harmonics are produced when
-
a resonant circuit is detuned (23% chose this)
-
negative feedback is applied to an amplifier (13% chose this)
-
a transistor is biased for class A operation (5% chose this)
-
a sine wave is distorted (59% chose this)
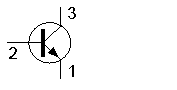
In the figure shown, 3 represents the
-
drain of a junction FET (7% chose this)
-
collector of an npn transistor (52% chose this)
-
emitter of a pnp transistor (32% chose this)
-
base of an npn transistor (9% chose this)
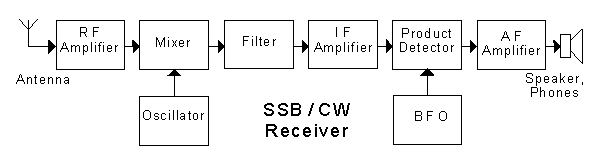
In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the output frequency of the "oscillator" is
-
the same as that of the incoming received signal (21% chose this)
-
the same as that of the IF frequency (28% chose this)
-
different from both the incoming signal and IF frequencies (49% chose this)
-
at a low audio frequency (2% chose this)
The frequency limits of the �70 centimetre band� are
-
430 to 440 MHz (52% chose this)
-
430 to 450 MHz (18% chose this)
-
435 to 438 MHz (18% chose this)
-
430 to 460 MHz (11% chose this)
The reactance of an inductor increases as the
-
frequency increases (53% chose this)
-
frequency decreases (23% chose this)
-
applied voltage increases (16% chose this)
-
applied voltage decreases (7% chose this)
Radio wave polarisation is defined by the orientation of the radiated
-
magnetic field (39% chose this)
-
electric field (47% chose this)
-
inductive field (12% chose this)
-
capacitive field (2% chose this)
If broadband noise interference varies when it rains, the most likely cause could be from
-
underground power cables (2% chose this)
-
outside overhead power lines (47% chose this)
-
car ignitions (2% chose this)
-
your antenna connection (49% chose this)
The current in a 100 kilohm resistor is 10 mA. The power dissipated is
-
1 watt (20% chose this)
-
10 watt (55% chose this)
-
100 watt (9% chose this)
-
10,000 watt (16% chose this)
Two 33 ohm resistors are connected in series with a power supply. If the current flowing is 100 mA, the voltage across one of the resistors is
-
66 volt (24% chose this)
-
33 volt (7% chose this)
-
3.3 volt (59% chose this)
-
1 volt (10% chose this)
The frequency limits of the �80 metre band� are
-
3.50 to 4.0 MHz (12% chose this)
-
3.50 to 3.90 MHz (48% chose this)
-
3.50 to 3.85 MHz (32% chose this)
-
3.6 to 3.9 MHz (8% chose this)
Two 20 uH inductances are connected in parallel. The total inductance is
-
10 uH (53% chose this)
-
20 uH (13% chose this)
-
40 uH (33% chose this)
-
80 uH (0% chose this)
In New Zealand the frequency limits of the �40 metre band� are
-
7.00 to 7.10 MHz (5% chose this)
-
7.00 to 7.15 MHz (24% chose this)
-
7.00 to 7.30 MHz (57% chose this)
-
7.10 to 7.40 MHz (14% chose this)
A good voltmeter should have
-
a very high internal resistance (53% chose this)
-
a resistance equal to that of all other components in the circuit (7% chose this)
-
a very low internal resistance (40% chose this)
-
an inductive reactance (0% chose this)
A residual current device is recommended for protection in a mains power circuit because it
-
reduces electrical interference from the circuit (4% chose this)
-
removes power to the circuit when the phase and neutral currents are not equal (51% chose this)
-
removes power to the circuit when the current in the phase wire equals the current in the earth wire (36% chose this)
-
limits the power provided to the circuit (9% chose this)
Three 15 picofarad capacitors are wired in parallel. The value of the combination is
-
45 picofarad (65% chose this)
-
18 picofarad (0% chose this)
-
12 picofarad (11% chose this)
-
5 picofarad (24% chose this)
To minimise the radiation of one particular harmonic, one can use a
-
wave trap in the transmitter output (44% chose this)
-
resistor (0% chose this)
-
high pass filter in the transmitter output (43% chose this)
-
filter in the receiver lead (13% chose this)
Two bands where amateur satellites may operate are
-
28.0 to 29.7 MHz and 144.0 to 146.0 MHz (59% chose this)
-
21.0 to 21.1 MHz and 146.0 to 148.0 MHz (20% chose this)
-
3.5 to 3.8 MHz and 7.0 to 7.1 MHz (7% chose this)
-
7.1 to 7.3 MHz and 10.1 to 10.15 MHz (15% chose this)
The question "Who is calling me?" is asked by
-
QRT? (19% chose this)
-
QRM? (10% chose this)
-
QRP? (14% chose this)
-
QRZ? (57% chose this)
Amateur stations are often regarded as "frequency agile". This means
-
operation is limited to frequency modulation (0% chose this)
-
operators can choose to operate anywhere on a shared band (36% chose this)
-
a bandswitch is required on all transceivers (3% chose this)
-
on a shared band operators can change frequency to avoid interfering (62% chose this)
Magnetic and electric fields about an antenna are
-
parallel to each other (10% chose this)
-
determined by the type of antenna used (29% chose this)
-
perpendicular to each other (57% chose this)
-
variable with the time of day (5% chose this)
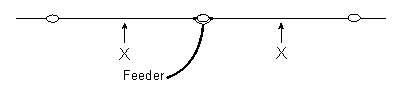
The physical length of the antenna shown in this diagram can be shortened and the electrical length maintained, if one of the following items is added at the points shown at 'X' in each wire
-
an inductor (60% chose this)
-
a capacitor (15% chose this)
-
an insulator (8% chose this)
-
a resistor (18% chose this)
A superhet receiver receives an incoming signal of 3540 kHz and the local oscillator produces a signal of 3995 kHz. The IF amplifier is tuned to
-
455 kHz (60% chose this)
-
3540 kHz (18% chose this)
-
3995 kHz (10% chose this)
-
7435 kHz (13% chose this)
The correct colour coding for the phase wire in a flexible mains lead is
-
brown (60% chose this)
-
blue (12% chose this)
-
yellow and green (12% chose this)
-
white (17% chose this)
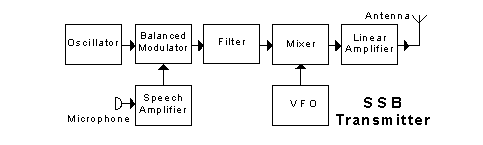
In the transmitter block diagram shown, the "oscillator"
-
is variable in frequency (33% chose this)
-
generates an audio frequency tone during tests (2% chose this)
-
uses a crystal for good frequency stability (56% chose this)
-
may have a calibrated dial (9% chose this)
An rms-reading voltmeter is used to measure a 50 Hz sinewave of known peak voltage 14 volt. The meter reading will be about
-
14 volt (24% chose this)
-
28 volt (14% chose this)
-
10 volt (60% chose this)
-
50 volt (2% chose this)
The power dissipation of a resistor carrying a current of 10 mA with 10 volt across it is
-
0.01 watt (14% chose this)
-
0.1 watt (51% chose this)
-
1 watt (31% chose this)
-
10 watt (4% chose this)
For long distance propagation, the radiation angle of energy from the antenna should be
-
less than 30 degrees (56% chose this)
-
more than 30 degrees but less than forty-five (24% chose this)
-
more than 45 degrees but less than ninety (13% chose this)
-
90 degrees (7% chose this)
"RIT" stands for
-
receiver interference transmuter (9% chose this)
-
range independent transmission (17% chose this)
-
receiver incremental tuning (62% chose this)
-
random interference tester (13% chose this)
The frequency limits of the �2 metre band� are
-
144 to 149 MHz (20% chose this)
-
144 to 148 MHz (64% chose this)
-
146 to 148 MHz (7% chose this)
-
144 to 150 MHz (9% chose this)
An RF amplifier ahead of the mixer stage in a superhet receiver
-
enables the receiver to tune a greater frequency range (16% chose this)
-
means no BFO stage is needed (8% chose this)
-
makes it possible to receive SSB signals (0% chose this)
-
increases the sensitivity of the receiver (76% chose this)
A half-wave antenna resonant at 7100 kHz is approximately this long
-
20 metres (58% chose this)
-
40 metres (30% chose this)
-
80 metres (8% chose this)
-
160 metres (4% chose this)
If a 12 volt battery supplies 0.15 ampere to a circuit, the circuit's resistance is
-
0.15 ohm (5% chose this)
-
1.8 ohm (16% chose this)
-
12 ohm (3% chose this)
-
80 ohm (76% chose this)
The AGC circuit in a receiver usually controls the
-
audio stage (38% chose this)
-
mixer stage (2% chose this)
-
power supply (0% chose this)
-
RF and IF stages (60% chose this)
The voltage drop across a germanium signal diode when conducting is about
-
0.3V (56% chose this)
-
0.6V (8% chose this)
-
0.7V (31% chose this)
-
1.3V (6% chose this)
A result of standing waves on a non-resonant transmission line is
-
maximum transfer of energy to the antenna from the transmitter (13% chose this)
-
perfect impedance match between transmitter and feedline (11% chose this)
-
reduced transfer of RF energy to the antenna (65% chose this)
-
lack of radiation from the transmission line (11% chose this)
Electrolytic capacitors are used in power supplies because
-
they are tuned to operate at 50 Hz (5% chose this)
-
they have very low losses compared to other types (25% chose this)
-
they radiate less RF noise than other types (15% chose this)
-
they can be obtained in larger values than other types (55% chose this)
Filter capacitors in power supplies are sometimes connected in series to
-
withstand a greater voltage than a single capacitor can withstand (65% chose this)
-
increase the total capacity (4% chose this)
-
reduce the ripple voltage further (22% chose this)
-
resonate the filter circuit (9% chose this)
A damaged antenna or feedline attached to the output of a transmitter will present an incorrect load resulting in
-
the driver stage not delivering power to the final (17% chose this)
-
the output tuned circuit breaking down (6% chose this)
-
excessive heat being produced in the transmitter output stage (64% chose this)
-
loss of modulation in the transmitted signal (13% chose this)
A 10 mA current is measured in a 500 ohm resistor. The voltage across the resistor will be
-
5 volt (65% chose this)
-
50 volt (24% chose this)
-
500 volt (2% chose this)
-
5000 volt (9% chose this)
A transmitting antenna for 28 MHz for mounting on the roof of a car could be a
-
vertical long wire (16% chose this)
-
quarter wave vertical (68% chose this)
-
horizontal dipole (14% chose this)
-
full wave centre fed horizontal (2% chose this)
A semiconductor is described as a "general purpose audio NPN device". This is a
-
triode (0% chose this)
-
silicon diode (11% chose this)
-
bipolar transistor (68% chose this)
-
field effect transistor (20% chose this)
The following is installed in the transmission line as close as possible to a HF transmitter to reduce harmonic output
-
a middle-pass filter (2% chose this)
-
a low-pass filter (71% chose this)
-
a high-pass filter (21% chose this)
-
a band-reject filter (5% chose this)

In this receiver, an audio frequency gain control would be associated with the block labelled
-
AF amplifier (65% chose this)
-
frequency demodulator (13% chose this)
-
speaker, phones (7% chose this)
-
IF amplifier (15% chose this)
Reception of high frequency radio waves beyond 4000 km normally occurs by the
-
ground wave (10% chose this)
-
skip wave (13% chose this)
-
surface wave (3% chose this)
-
sky wave (75% chose this)
To reduce energy from an HF transmitter getting into a television receiver, the following could be placed in the TV antenna lead as close to the TV as possible
-
active filter (2% chose this)
-
low-pass filter (22% chose this)
-
high-pass filter (61% chose this)
-
band reject filter (16% chose this)
The radio wave from the transmitter to the ionosphere and back to earth is correctly known as the
-
sky wave (63% chose this)
-
skip wave (35% chose this)
-
surface wave (0% chose this)
-
F layer (2% chose this)
The wavelength for a frequency of 25 MHz is
-
15 metres (13% chose this)
-
32 metres (10% chose this)
-
4 metres (13% chose this)
-
12 metres (65% chose this)
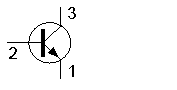
In the figure shown, 2 represents the
-
collector of a pnp transistor (7% chose this)
-
emitter of an npn transistor (16% chose this)
-
base of an npn transistor (69% chose this)
-
source of a junction FET (9% chose this)

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the "mixer"
-
changes the signal frequency (76% chose this)
-
rejects SSB and CW signals (2% chose this)
-
protects against receiver overload (0% chose this)
-
limits the noise on the signal (22% chose this)
Impedance is a combination of
-
reactance with reluctance (8% chose this)
-
resistance with conductance (25% chose this)
-
resistance with reactance (65% chose this)
-
reactance with radiation (2% chose this)
Regular changes in the ionosphere occur approximately every 11
-
days (24% chose this)
-
months (2% chose this)
-
years (74% chose this)
-
centuries (0% chose this)
Excessive harmonic output may be produced in a transmitter by
-
a linear amplifier (7% chose this)
-
a low SWR (0% chose this)
-
resonant circuits (19% chose this)
-
overdriven amplifier stages (74% chose this)
The "Q signal" requesting the other station to send slower is
-
QRL (12% chose this)
-
QRN (2% chose this)
-
QRM (10% chose this)
-
QRS (76% chose this)
As temperature increases, the resistance of a metallic conductor
-
increases (56% chose this)
-
decreases (42% chose this)
-
remains constant (2% chose this)
-
becomes negative (0% chose this)
Resistors of 68 ohm, 47 kilohm, 560 ohm and 10 ohm are connected in parallel. The total resistance is
-
less than 10 ohm (79% chose this)
-
between 68 and 560 ohm (8% chose this)
-
between 560 and and 47 kilohm (3% chose this)
-
greater than 47 kilohm (10% chose this)
Changes in received signal strength when sky wave propagation is used are called
-
ground wave losses (3% chose this)
-
modulation losses (11% chose this)
-
fading (84% chose this)
-
sunspots (3% chose this)
Of two receivers, the one capable of receiving the weakest signal will have
-
an RF gain control (33% chose this)
-
the least internally-generated noise (60% chose this)
-
the loudest audio output (2% chose this)
-
the greatest tuning range (6% chose this)
A bipolar transistor has three terminals named
-
base, emitter and drain (20% chose this)
-
collector, base and source (2% chose this)
-
emitter, base and collector (67% chose this)
-
drain, source and gate (11% chose this)
The frequency limits of the �20 metre band� are
-
14.00 to 14.10 MHz (7% chose this)
-
14.00 to 14.45 MHz (19% chose this)
-
14.00 to 14.50 MHz (17% chose this)
-
14.00 to 14.35 MHz (57% chose this)
If a 3 volt battery causes 300 mA to flow in a circuit, the circuit resistance is
-
10 ohm (70% chose this)
-
9 ohm (23% chose this)
-
5 ohm (0% chose this)
-
3 ohm (7% chose this)
In a regulated power supply, the 'crowbar' is a
-
means to lever up the output voltage (17% chose this)
-
circuit for testing mains fuses (2% chose this)
-
last-ditch protection against failure of the regulator in the supply (74% chose this)
-
convenient means to move such a heavy supply unit (7% chose this)
In a forward biased pn junction, the electrons
-
flow from p to n (40% chose this)
-
flow from n to p (60% chose this)
-
remain in the n region (0% chose this)
-
remain in the p region (0% chose this)
A VSWR meter switched to the "reverse" position provides an indication of
-
power output in watts (12% chose this)
-
relative reflected voltage (62% chose this)
-
relative forward voltage (6% chose this)
-
reflected power in dB (21% chose this)
One important application for diodes is recovering information from transmitted signals. This is referred to as
-
biasing (20% chose this)
-
rejuvenation (2% chose this)
-
ionisation (0% chose this)
-
demodulation (78% chose this)
Bipolar transistors usually have
-
4 connecting leads (8% chose this)
-
3 connecting leads (62% chose this)
-
2 connecting leads (31% chose this)
-
1 connecting lead (0% chose this)
The "squelch" or "muting" circuitry on a VHF receiver
-
inhibits the audio output unless a station is being received (67% chose this)
-
compresses incoming voice signals to make them more intelligible (0% chose this)
-
reduces audio burst noise due to lightning emissions (4% chose this)
-
reduces the noise on incoming signals (29% chose this)
Three good electrical conductors are
-
copper, gold, mica (13% chose this)
-
gold, silver, wood (0% chose this)
-
gold, silver, aluminium (82% chose this)
-
copper, aluminium, paper (5% chose this)
A transformer with 100 turns on the primary winding and 10 turns on the secondary winding is connected to 230 volt AC mains. The voltage across the secondary is
-
10 volt (14% chose this)
-
23 volt (74% chose this)
-
110 volt (2% chose this)
-
2300 volt (9% chose this)
The layer of the ionosphere mainly responsible for long distance communication is
-
C (4% chose this)
-
D (14% chose this)
-
E (18% chose this)
-
F (64% chose this)
The 'rms value' of a sine-wave signal is
-
half the peak voltage (3% chose this)
-
1.414 times the peak voltage (13% chose this)
-
the peak-to-peak voltage (5% chose this)
-
0.707 times the peak voltage (80% chose this)
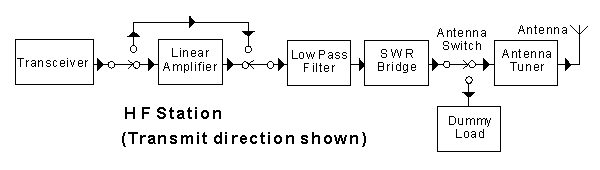
In the block diagram shown, the "dummy load" is
-
used to allow adjustment of the transmitter without causing interference to others (84% chose this)
-
a load used to absorb surplus power which is rejected by the antenna system (16% chose this)
-
used to absorb high-voltage impulses caused by lightning strikes to the antenna (0% chose this)
-
an additional load used to compensate for a badly-tuned antenna system (0% chose this)
Which of the following is most likely to cause broad-band continuous interference
-
an electric blanket switch (2% chose this)
-
a refrigerator thermostat (4% chose this)
-
a microwave transmitter (26% chose this)
-
poor commutation in an electric motor (68% chose this)
Two resistors are connected in parallel. R1 is 75 ohm and R2 is 50 ohm. The total resistance of this parallel circuit is
-
10 ohm (4% chose this)
-
70 ohm (8% chose this)
-
30 ohm (64% chose this)
-
40 ohm (24% chose this)
A 28 MHz radio signal is more likely to be heard over great distances
-
if the transmitter power is reduced (4% chose this)
-
during daylight hours (65% chose this)
-
only during the night (29% chose this)
-
at full moon (2% chose this)
The usual effect of ionospheric storms is to
-
increase the maximum usable frequency (27% chose this)
-
cause a fade-out of sky-wave signals (67% chose this)
-
produce extreme weather changes (2% chose this)
-
prevent communications by ground wave (4% chose this)
A neighbour's stereo system is suffering RF break-through. One possible cure is to
-
put a ferrite bead on the transmitter output lead (38% chose this)
-
put a capacitor across the transmitter output (4% chose this)
-
use open-wire feeders to the antenna (2% chose this)
-
use screened wire for the loudspeaker leads (57% chose this)
A 6 ohm resistor is connected in parallel with a 30 ohm resistor. The total resistance of the combination is
-
5 ohm (80% chose this)
-
8 ohm (8% chose this)
-
24 ohm (13% chose this)
-
35 ohm (0% chose this)
The 'critical frequency' is defined as the
-
highest frequency to which your transmitter can be tuned (9% chose this)
-
lowest frequency which is reflected back to earth at vertical incidence (17% chose this)
-
minimum usable frequency (4% chose this)
-
highest frequency which will be reflected back to earth at vertical incidence (70% chose this)
The fundamental regulations controlling the Amateur Service are to be found in
-
the International Radio Regulations from the ITU (67% chose this)
-
the Radio Amateur's Handbook (15% chose this)
-
the NZART Callbook (19% chose this)
-
on the packet radio bulletin-board (0% chose this)
The total resistance of several resistors connected in series is
-
less than the resistance of any one resistor (6% chose this)
-
greater than the resistance of any one resistor (89% chose this)
-
equal to the highest resistance present (0% chose this)
-
equal to the lowest resistance present (6% chose this)
Which of the following operating arrangements allows a NZ citizen holding a General Amateur Operator�s Certificate of Competency and a call-sign to operate in many European countries
-
CEPT agreement (48% chose this)
-
IARP agreement (2% chose this)
-
ITU reciprocal license (27% chose this)
-
All of these choices are correct (23% chose this)
The following resistor combination can most nearly replace a single 150 ohm resistor
-
four 47 ohm resistors in parallel (9% chose this)
-
five 33 ohm resistors in parallel (9% chose this)
-
three 47 ohm resistors in series (68% chose this)
-
five 33 ohm resistors in series (15% chose this)
The resonant frequency of an antenna may be increased by
-
shortening the radiating element (70% chose this)
-
lengthening the radiating element (26% chose this)
-
increasing the height of the radiating element (4% chose this)
-
lowering the radiating element (0% chose this)
An ohmmeter measures the
-
value of any resistance placed between its terminals (70% chose this)
-
impedance of any component placed between its terminals (15% chose this)
-
power factor of any inductor or capacitor placed between its terminals (2% chose this)
-
voltage across any resistance placed between its terminals (13% chose this)
A General Amateur Operator Certificate of Competency holder must advise permanent changes to postal and email addresses and update the official database records within
-
One Calendar month (79% chose this)
-
7 days (12% chose this)
-
10 days (2% chose this)
-
one year (7% chose this)

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the "product detector"
-
produces an 800 Hz beat note (9% chose this)
-
separates CW and SSB signals (15% chose this)
-
rejects AM signals (6% chose this)
-
translates signals to audio frequencies (70% chose this)
A toroidal inductor is one in which the
-
windings are wound on a closed ring of magnetic material (72% chose this)
-
windings are air-spaced (0% chose this)
-
windings are wound on a ferrite rod (22% chose this)
-
inductor is enclosed in a magnetic shield (7% chose this)
To lower the resonant frequency of an antenna, the operator should
-
lengthen the antenna (66% chose this)
-
centre feed the antenna with TV ribbon (0% chose this)
-
shorten the antenna (28% chose this)
-
ground one end (6% chose this)
A superhet receiver, with an IF at 500 kHz, is receiving a 14 MHz signal. The local oscillator frequency is
-
14.5 MHz (69% chose this)
-
19 MHz (2% chose this)
-
500 kHz (10% chose this)
-
28 MHz (19% chose this)
Amateur radio repeater equipment and frequencies in New Zealand are co-ordinated by
-
the Ministry of Business, Innovation, and Employment (26% chose this)
-
NZART branches in the main cities (6% chose this)
-
repeater trustees (6% chose this)
-
the NZART Frequency Management and Technical Advisory Group. (62% chose this)
If the height of the reflecting layer of the ionosphere increases, the skip distance of a high frequency transmission
-
stays the same (2% chose this)
-
decreases (12% chose this)
-
varies regularly (7% chose this)
-
becomes greater (79% chose this)
This voltage is needed to cause a current of 200 mA to flow in a lamp of 25 ohm resistance
-
5 volt (79% chose this)
-
8 volt (10% chose this)
-
175 volt (2% chose this)
-
225 volt (10% chose this)
A radio wave may follow two or more different paths during propagation and produce slowly-changing phase differences between signals at the receiver resulting in a phenomenon called
-
absorption (2% chose this)
-
baffling (2% chose this)
-
fading (72% chose this)
-
skip (24% chose this)
The highest frequency that will be reflected back to the earth at any given time is known as the
-
UHF (20% chose this)
-
MUF (73% chose this)
-
OWF (2% chose this)
-
LUF (4% chose this)
VHF and UHF bands are frequently used for satellite communication because
-
waves at these frequencies travel to and from the satellite relatively unaffected by the ionosphere (85% chose this)
-
the Doppler frequency change caused by satellite motion is much less than at HF (10% chose this)
-
satellites move too fast for HF waves to follow (3% chose this)
-
the Doppler effect would cause HF waves to be shifted into the VHF and UHF bands. (3% chose this)

In the block diagram shown, the "SWR bridge" is a
-
switched wave rectifier for monitoring power output (18% chose this)
-
static wave reducer to minimize static electricity from the antenna (7% chose this)
-
device to monitor the standing-wave-ratio on the antenna feedline (73% chose this)
-
short wave rectifier to protect against lightning strikes (2% chose this)
Each of 9 resistors in a circuit is dissipating 4 watt. If the circuit operates from a 12 volt supply, the total current flowing in the circuit is
-
48 ampere (4% chose this)
-
36 ampere (23% chose this)
-
9 ampere (2% chose this)
-
3 ampere (70% chose this)
A low-level signal is applied to a transistor circuit input and a higher-level signal is present at the output. This effect is known as
-
amplification (92% chose this)
-
detection (3% chose this)
-
modulation (0% chose this)
-
rectification (6% chose this)
An atom that loses an electron becomes
-
a positive ion (58% chose this)
-
an isotope (4% chose this)
-
a negative ion (33% chose this)
-
a radioactive atom (5% chose this)
Cross-modulation of a broadcast receiver by a nearby transmitter would be noticed in the receiver as
-
a lack of signals being received (2% chose this)
-
the undesired signal in the background of the desired signal (73% chose this)
-
interference only when a broadcast signal is received (20% chose this)
-
distortion on transmitted voice peaks (4% chose this)
The minimum age for a person to hold a General Amateur Operator Certificate of Competency is
-
12 years (7% chose this)
-
16 years (14% chose this)
-
21 years (0% chose this)
-
there is no age limit (79% chose this)
General Amateur Operator Certificates of Competency and callsigns are issued pursuant to the Regulations by the
-
New Zealand Association of Radio Transmitters (NZART) (33% chose this)
-
Ministry of Business, Innovation, and Employment Approved Radio Examiners (62% chose this)
-
Department of Internal Affairs (4% chose this)
-
Prime Minister's Office (2% chose this)
One quarter of one ampere may be written as
-
250 microampere (2% chose this)
-
0.5 ampere (0% chose this)
-
0.25 milliampere (20% chose this)
-
250 milliampere (77% chose this)
In an atom
-
the protons and the neutrons orbit the nucleus in opposite directions (6% chose this)
-
the protons orbit around the neutrons (6% chose this)
-
the electrons orbit the nucleus (72% chose this)
-
the electrons and the neutrons orbit the nucleus (15% chose this)
Installing a low-pass filter between the transmitter and transmission line will
-
permit higher frequency signals to pass to the antenna (17% chose this)
-
ensure an SWR not exceeding 2:1 (4% chose this)
-
reduce the power output back to the legal maximum (6% chose this)
-
permit lower frequency signals to pass to the antenna (72% chose this)
An antenna which transmits equally well in all compass directions is a
-
dipole with a reflector only (8% chose this)
-
quarterwave grounded vertical (71% chose this)
-
dipole with director only (0% chose this)
-
half-wave horizontal dipole (21% chose this)
When measuring the current drawn by a light bulb from a DC supply, the meter will act in circuit as
-
an insulator (4% chose this)
-
a low value resistance (68% chose this)
-
a perfect conductor (22% chose this)
-
an extra current drain (6% chose this)
Two basic types of bipolar transistors are
-
p-channel and n-channel types (14% chose this)
-
NPN and PNP types (81% chose this)
-
diode and triode types (2% chose this)
-
varicap and zener types (2% chose this)
A qualified operator of an amateur radio station may permit anyone to
-
operate the station under direct supervision (35% chose this)
-
send business traffic to any other station. (4% chose this)
-
pass brief comments of a personal nature provided no fees or other considerations are requested or accepted (62% chose this)
-
use the station for Morse sending practice (0% chose this)
A filter used to attenuate a very narrow band of frequencies centred on 3.6 MHz would be called
-
a band-pass filter (19% chose this)
-
a high-pass filter (2% chose this)
-
a low-pass filter (6% chose this)
-
a notch filter (72% chose this)
Two amplifiers with gains of 10 dB and 40 dB are connected in cascade. The gain of the combination is
-
8 dB (0% chose this)
-
30 dB (9% chose this)
-
50 dB (77% chose this)
-
400 dB (14% chose this)
The following feeder is the best match to the base of a quarter wave ground plane antenna
-
300 ohm balanced feedline (9% chose this)
-
50 ohm coaxial cable (72% chose this)
-
75 ohm balanced feedline (17% chose this)
-
300 ohm coaxial cable (2% chose this)
A high-pass filter attenuates
-
a band of frequencies in the VHF region (2% chose this)
-
all except a band of VHF frequencies (2% chose this)
-
high frequencies but not low frequencies (32% chose this)
-
low frequencies but not high frequencies (64% chose this)
A high-pass filter can be used to
-
prevent interference to a telephone (0% chose this)
-
prevent overmodulation in a transmitter (10% chose this)
-
prevent interference to a TV receiver (65% chose this)
-
pass a band of speech frequencies in a modulator (25% chose this)
Several stations advise that your FM simplex transmission in the "two metre" band is distorted. The cause might be that
-
the transmitter modulation deviation is too high (65% chose this)
-
your antenna is too low (10% chose this)
-
the transmitter has become unsynchronised (13% chose this)
-
your transmitter frequency split is incorrect (12% chose this)
The holder of a General Amateur Operator Certificate of Competency may permit anyone to
-
use an amateur radio station to communicate with other radio amateurs (16% chose this)
-
pass brief messages of a personal nature provided no fees or other consideration are requested or accepted (62% chose this)
-
operate the amateur station under the supervision and in the presence of a qualified operator (22% chose this)
-
take part in communications only if prior written permission is received from the Ministry of Business, Innovation, and Employment (0% chose this)
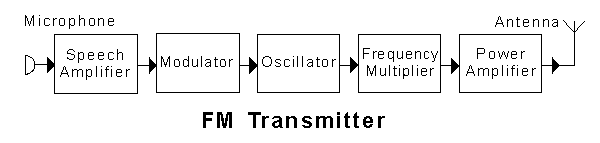
In the transmitter block diagram shown, the "power amplifier"
-
increases the voltage of the mains to drive the antenna (5% chose this)
-
amplifies the audio frequency component of the signal (8% chose this)
-
amplifies the selected sideband to a suitable level (3% chose this)
-
amplifies the RF signal to a suitable level (85% chose this)
The mixer stage of a superhet receiver
-
produces spurious signals (2% chose this)
-
produces an intermediate frequency signal (79% chose this)
-
acts as a buffer stage (2% chose this)
-
demodulates SSB signals (16% chose this)
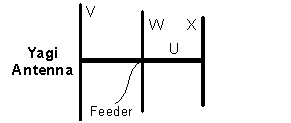
In this diagram the item U corresponds to the
-
boom (79% chose this)
-
reflector (2% chose this)
-
driven element (7% chose this)
-
director (12% chose this)
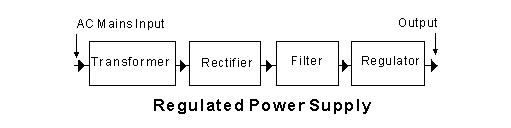
The block marked 'Regulator' in the diagram is to
-
regulate the incoming mains voltage to a constant value (6% chose this)
-
ensure that the output voltage never exceeds a dangerous value (15% chose this)
-
keep the incoming frequency constant at 50 Hz (6% chose this)
-
keep the output voltage at a constant value (72% chose this)
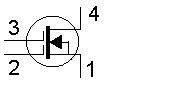
The figure shown represents a
-
dual bipolar transistor (12% chose this)
-
dual diode (9% chose this)
-
dual varactor diode (0% chose this)
-
dual gate MOSFET (79% chose this)
When conversing via a VHF or UHF repeater you should pause between overs for about
-
half a second (20% chose this)
-
3 seconds (76% chose this)
-
30 seconds (2% chose this)
-
several minutes (2% chose this)
The voltage 'two volt' is also
-
2000 mV (77% chose this)
-
2000 kV (16% chose this)
-
2000 uV (5% chose this)
-
2000 MV (2% chose this)

The antenna in this diagram can be made to operate on several bands if the following item is installed at the points shown at 'X' in each wire
-
a capacitor (4% chose this)
-
an inductor (24% chose this)
-
a fuse (2% chose this)
-
a parallel-tuned trap (69% chose this)
You can operate this number of identical lamps, each drawing a current of 250 mA, from a 5A supply
-
50 (23% chose this)
-
30 (0% chose this)
-
20 (72% chose this)
-
5 (4% chose this)

The block marked 'Filter' in the diagram is to
-
filter RF radiation from the output of the power supply (24% chose this)
-
smooth the rectified waveform from the rectifier (68% chose this)
-
act as a 50 Hz tuned circuit (6% chose this)
-
restore voltage variations (2% chose this)
Although high frequency signals may be received from a distant station by a sky wave at a certain time, it may not be possible to hear them an hour later. This may be due to
-
changes in the ionosphere (79% chose this)
-
shading of the earth by clouds (2% chose this)
-
changes in atmospheric temperature (7% chose this)
-
absorption of the ground wave signal (12% chose this)

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the "BFO" stands for
-
bad frequency obscurer (0% chose this)
-
basic frequency oscillator (2% chose this)
-
beat frequency oscillator (76% chose this)
-
band filter oscillator (22% chose this)
Narrow-band interference can be caused by
-
transmitter harmonics (63% chose this)
-
a neon sign (20% chose this)
-
a shaver motor (9% chose this)
-
lightning flashes (9% chose this)
The material separating the plates of a capacitor is the
-
dielectric (88% chose this)
-
semiconductor (8% chose this)
-
resistor (0% chose this)
-
lamination (5% chose this)

In this block diagram, the block designated "antenna tuner" is not normally necessary when
-
the antenna input impedance is 50 ohms (70% chose this)
-
a half wave antenna is used, fed at one end (20% chose this)
-
the antenna is very long compared to a wavelength (8% chose this)
-
the antenna is very short compared to a wavelength (2% chose this)
For regulatory purposes the world is divided into regions each with different radio spectrum allocations. New Zealand is in
-
Region 1 (7% chose this)
-
Region 2 (5% chose this)
-
Region 3 (61% chose this)
-
Region 4 (26% chose this)
A high-pass RF filter would normally be fitted
-
between transmitter output and feedline (31% chose this)
-
at the antenna terminals of a TV receiver (59% chose this)
-
at the Morse key or keying relay in a transmitter (2% chose this)
-
between microphone and speech amplifier (8% chose this)
The following formula gives the resistance of a circuit
-
R = I / E [resistance equals current divided by voltage] (13% chose this)
-
R = E x I [resistance equals voltage times current (10% chose this)
-
R = E / R [resistance equals voltage divided by resistance] (4% chose this)
-
R = E / I [resistance equals voltage divided by current] (73% chose this)
If the frequency of a transmitted signal is so high that we no longer receive a reflection from the ionosphere, the signal frequency is above the
-
speed of light (0% chose this)
-
sun spot frequency (4% chose this)
-
skip distance (20% chose this)
-
maximum usable frequency (76% chose this)
That portion of HF radiation which is directly affected by the surface of the earth is called
-
ionospheric wave (21% chose this)
-
local field wave (2% chose this)
-
ground wave (74% chose this)
-
inverted wave (2% chose this)
This commonly available antenna feedline can be buried directly in the ground for some distance without adverse effects
-
75 ohm twinlead (5% chose this)
-
300 ohm twinlead (3% chose this)
-
600 ohm open-wire (5% chose this)
-
coaxial cable (88% chose this)
The unit of inductance is the
-
farad (11% chose this)
-
henry (80% chose this)
-
ohm (7% chose this)
-
reactance (2% chose this)
The resonant frequency of a dipole antenna is mainly determined by
-
its height above the ground (0% chose this)
-
its length (97% chose this)
-
the output power of the transmitter used (3% chose this)
-
the length of the transmission line (0% chose this)
The accepted way to call "CQ" with a SSB transceiver is
-
"CQ CQ CQ this is ZL1XXX ZL1XXX ZL1XXX" (92% chose this)
-
"This is ZL1XXX calling CQ CQ CQ" (8% chose this)
-
"CQ to anyone, CQ to anyone, I am ZL1XXX" (0% chose this)
-
"CQ CQ CQ CQ CQ this is New Zealand" (0% chose this)
This many 12 volt bulbs can be arranged in series to form a string of lights to operate from a 240 volt power supply
-
12 x 240 (10% chose this)
-
240 + 12 (5% chose this)
-
240 - 12 (0% chose this)
-
240 / 12 (85% chose this)
The characteristic impedance of a 20 metre length of transmission line is 52 ohm. If 10 metres is cut off, the impedance will be
-
13 ohm (2% chose this)
-
26 ohm (33% chose this)
-
39 ohm (0% chose this)
-
52 ohm (65% chose this)
SSB transmissions
-
occupy about twice the bandwidth of AM transmissions (22% chose this)
-
contain more information than AM transmissions (2% chose this)
-
occupy about half the bandwidth of AM transmissions (71% chose this)
-
are compatible with FM transmissions (4% chose this)
A licence that provides for a given class of radio transmitter to be used without requiring a licence in the owner�s own name is known as
-
a repeater licence (20% chose this)
-
a general user radio licence (69% chose this)
-
a beacon licence (4% chose this)
-
a reciprocal licence (8% chose this)
Harmonics produced in an early stage of a transmitter may be reduced in a later stage by
-
increasing the signal input to the final stage (8% chose this)
-
using FET power amplifiers (8% chose this)
-
using tuned circuit coupling between stages (70% chose this)
-
using larger value coupling capacitors (14% chose this)
A General Amateur Operator Certificate of Competency
-
expires after 6 months (0% chose this)
-
contains the unique callsign(s) to be used by that operator (71% chose this)
-
is transferable (2% chose this)
-
permits the transmission of radio waves (27% chose this)
When two 1000 ohm 5 watt resistors are connected in parallel, they can dissipate a maximum total power of
-
40 watt (2% chose this)
-
20 watt (6% chose this)
-
10 watt (69% chose this)
-
5 watt (24% chose this)
The basic semiconductor amplifying device is a
-
diode (7% chose this)
-
transistor (85% chose this)
-
pn-junction (5% chose this)
-
silicon gate (2% chose this)
A common use for a magnet is in
-
A computer speaker (82% chose this)
-
An optical mouse (0% chose this)
-
A keyboard (0% chose this)
-
A magnetic loop antenna (18% chose this)
You hear a station using the callsign �VK3XYZ stroke ZL� on your local VHF repeater. This is
-
a callsign not authorised for use in New Zealand (7% chose this)
-
a confused illegal operator (5% chose this)
-
the station of an overseas visitor (88% chose this)
-
probably an unlicensed person using stolen equipment (0% chose this)
This combination of series resistors could replace a single 120 ohm resistor
-
five 24 ohm (78% chose this)
-
six 22 ohm (4% chose this)
-
two 62 ohm (17% chose this)
-
five 100 ohm (0% chose this)
The correct colour coding for the earth wire in a flexible mains lead is
-
brown (8% chose this)
-
blue (0% chose this)
-
yellow and green (90% chose this)
-
white (3% chose this)

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the "mixer"
-
combines signals at two different frequencies to produce one at an intermediate frequency (73% chose this)
-
combines sidebands to produce a stronger signal (10% chose this)
-
discriminates against SSB and AM signals (4% chose this)
-
inserts a carrier wave to produce a true FM signal (12% chose this)
The element Silicon is
-
a conductor (2% chose this)
-
an insulator (5% chose this)
-
a superconductor (11% chose this)
-
a semiconductor (82% chose this)
Capacitors and inductors oppose an alternating current. This is known as
-
resistance (8% chose this)
-
resonance (13% chose this)
-
conductance (4% chose this)
-
reactance (75% chose this)

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the "filter" rejects
-
AM and RTTY signals (9% chose this)
-
unwanted mixer outputs (84% chose this)
-
noise bursts (7% chose this)
-
broadcast band signals (0% chose this)
Three 500 ohm resistors are wired in series. Short-circuiting the centre resistor will change the value of the network from
-
1500 ohm to 1000 ohm (82% chose this)
-
500 ohm to 1000 ohm (9% chose this)
-
1000 ohm to 500 ohm (5% chose this)
-
1000 ohm to 1500 ohm (5% chose this)

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the "IF amplifier" is an
-
isolation frequency amplifier (13% chose this)
-
intelligence frequency amplifier (4% chose this)
-
indeterminate frequency amplifier (6% chose this)
-
intermediate frequency amplifier (77% chose this)
An amateur station must have a qualified operator
-
only when training another amateur (0% chose this)
-
whenever the station receiver is operated (11% chose this)
-
whenever the station is used for transmitting (77% chose this)
-
when transmitting and receiving (13% chose this)
The total current in a parallel circuit is equal to the
-
current in any one of the parallel branches (9% chose this)
-
sum of the currents through all the parallel branches (77% chose this)
-
applied voltage divided by the value of one of the resistive elements (4% chose this)
-
source voltage divided by the sum of the resistive elements (11% chose this)
The term "amateur third party communications" refers to
-
a simultaneous communication between three operators (0% chose this)
-
the transmission of commercial or secret messages (0% chose this)
-
messages to or on behalf of non-licensed people or organisations (84% chose this)
-
none of the above (16% chose this)
A transmitter power amplifier requires 30 mA at 300 volt. The DC input power is
-
300 watt (12% chose this)
-
9000 watt (15% chose this)
-
9 watt (69% chose this)
-
6 watt (4% chose this)
The process of modulation allows
-
information to be impressed on to a carrier (90% chose this)
-
information to be removed from a carrier (3% chose this)
-
voice and Morse code to be combined (3% chose this)
-
none of these (5% chose this)
The total resistance of four 68 ohm resistors wired in parallel is
-
12 ohm (8% chose this)
-
17 ohm (69% chose this)
-
34 ohm (12% chose this)
-
272 ohm (12% chose this)
Losses occurring on a transmission line between a transmitter and antenna result in
-
less RF power being radiated (90% chose this)
-
a SWR of 1:1 (3% chose this)
-
reflections occurring in the line (8% chose this)
-
improved transfer of RF energy to the antenna (0% chose this)
A new amateur radio operator is permitted to
-
operate on all amateur bands other than VHF at least weekly using a computer for log-keeping (0% chose this)
-
operate only on specified amateur bands for 3 months logging at least 50 contacts and retaining the log book for at least one year for possible official inspection (71% chose this)
-
operate only on one fixed frequency in the amateur bands between 5 and 25 MHz for 6 months and then present the log book for official inspection (14% chose this)
-
operate on amateur bands between 5 and 25 MHz as and when the operator chooses (16% chose this)
The three leads from a PNP transistor are named the
-
collector, source, drain (14% chose this)
-
gate, source, drain (16% chose this)
-
drain, base, source (0% chose this)
-
collector, emitter, base (71% chose this)
Scattered patches of high ionisation developed seasonally at the height of one of the layers is called
-
sporadic-E (80% chose this)
-
patchy (4% chose this)
-
random reflectors (2% chose this)
-
trans-equatorial ionisation (13% chose this)
A sine-wave alternating current of 10 ampere peak has an rms value of
-
5 amp (5% chose this)
-
7.07 amp (86% chose this)
-
14.14 amp (5% chose this)
-
20 amp (5% chose this)
The third harmonic of 7 MHz is
-
10 MHz (2% chose this)
-
14 MHz (8% chose this)
-
21 MHz (74% chose this)
-
28 MHz (16% chose this)
Harmonic frequencies are
-
always lower in frequency than the fundamental frequency (0% chose this)
-
at multiples of the fundamental frequency (88% chose this)
-
any unwanted frequency above the fundamental frequency (7% chose this)
-
any frequency causing TVI (5% chose this)

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the "AF amplifier"
-
amplifies stereo signals (14% chose this)
-
amplifies speech frequencies (73% chose this)
-
is an all frequency amplifier (12% chose this)
-
must be fitted with a tone control (2% chose this)
A rare DX station calling CQ on CW and repeating "up 2" at the end of the call means the station
-
will be listening for replies 2 kHz higher in frequency (77% chose this)
-
will reply only to stations sending at greater than 20 wpm (2% chose this)
-
is about to shift his calling frequency 2 kHz higher (19% chose this)
-
will wait more than 2 seconds before replying to his call (2% chose this)
The path radio waves normally follow from a transmitting antenna to a receiving antenna at VHF and higher frequencies is a
-
circular path going north or south from the transmitter (6% chose this)
-
great circle path (2% chose this)
-
straight line (79% chose this)
-
bent path via the ionosphere (13% chose this)
An important factor to consider when high angle radiation is desired from a horizontal half-wave antenna is the
-
size of the antenna wire (6% chose this)
-
time of the year (4% chose this)
-
height of the antenna (79% chose this)
-
mode of propagation (11% chose this)

In this diagram the item X corresponds to the
-
boom (4% chose this)
-
reflector (10% chose this)
-
director (77% chose this)
-
driven element (8% chose this)
The signal "QRM" means
-
your signals are fading (13% chose this)
-
I am troubled by static (11% chose this)
-
your transmission is being interfered with (67% chose this)
-
is my transmission being interfered with? (9% chose this)
A component is identified as a capacitor if its value is measured in
-
microvolts (2% chose this)
-
millihenrys (7% chose this)
-
megohms (7% chose this)
-
microfarads (84% chose this)
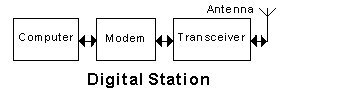
In the block diagram shown, the "modem"
-
monitors the demodulated signals (5% chose this)
-
de-emphasises the modulated data (0% chose this)
-
translates digital signals to and from audio signals (90% chose this)
-
determines the modulation protocol (5% chose this)
An electric current passing through a wire will produce around the conductor
-
an electric field (14% chose this)
-
a magnetic field (86% chose this)
-
an electrostatic field (0% chose this)
-
nothing (0% chose this)
If you transmit from another amateur's station, the person responsible for its proper operation is
-
both of you (11% chose this)
-
the other amateur (the station�s owner) (9% chose this)
-
you, the operator (67% chose this)
-
the station owner, unless the station records show that you were the operator at the time (13% chose this)

In this diagram the item V corresponds to the
-
boom (2% chose this)
-
reflector (79% chose this)
-
driven element (9% chose this)
-
director (11% chose this)
A half-wave antenna is often called a
-
bi-polar (2% chose this)
-
Yagi (2% chose this)
-
dipole (90% chose this)
-
beam (5% chose this)
The term describing opposition to electron flow in a metallic circuit is
-
current (8% chose this)
-
voltage (0% chose this)
-
resistance (93% chose this)
-
power (0% chose this)
The maximum radiation from a three element Yagi antenna is
-
in the direction of the reflector end of the boom (10% chose this)
-
in the direction of the director end of the boom (71% chose this)
-
at right angles to the boom (15% chose this)
-
parallel to the line of the coaxial feeder (4% chose this)
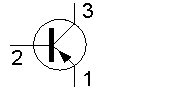
In the figure shown, 2 represents the
-
base of a pnp transistor (71% chose this)
-
drain of a junction FET (2% chose this)
-
gate of a junction FET (8% chose this)
-
emitter of a pnp transistor (19% chose this)
A result of mismatch between the power amplifier of a transmitter and the antenna is
-
reduced antenna radiation (82% chose this)
-
radiation of key clicks (7% chose this)
-
lower modulation percentage (4% chose this)
-
smaller DC current drain (7% chose this)
The DC input power of a transmitter operating at 12 volt and drawing 500 milliamp would be
-
6 watt (90% chose this)
-
12 watt (5% chose this)
-
20 watt (5% chose this)
-
500 watt (0% chose this)
The transmission of messages in a secret code by the operator of an amateur station is
-
permitted when communications are transmitted on behalf of a government agency (9% chose this)
-
permitted when communications are transmitted on behalf of third parties (4% chose this)
-
permitted during amateur radio contests (7% chose this)
-
not permitted except for control signals by the licensees of remote beacon or repeater stations (80% chose this)
The output voltage of a DC power supply decreases when current is drawn from it because
-
drawing output current causes the input mains voltage to decrease (10% chose this)
-
drawing output current causes the input mains frequency to decrease (10% chose this)
-
all power supplies have some internal resistance (74% chose this)
-
some power is reflected back into the mains. (6% chose this)
The unit of resistance is the
-
farad (0% chose this)
-
watt (0% chose this)
-
ohm (93% chose this)
-
resistor (8% chose this)
If ten resistors of equal value R are wired in parallel, the total resistance is
-
R (0% chose this)
-
10R (9% chose this)
-
10/R (22% chose this)
-
R/10 (69% chose this)
A signal report of "5 and 1" indicates
-
very low intelligibility but good signal strength (13% chose this)
-
perfect intelligibility but very low signal strength (84% chose this)
-
perfect intelligibility, high signal strength (0% chose this)
-
medium intelligibilty and signal strength (2% chose this)
The prime document for the administration of the Amateur Service in New Zealand is the
-
New Zealand Radiocommunications Regulations (81% chose this)
-
Broadcasting Act (9% chose this)
-
Radio Amateur's Handbook (2% chose this)
-
minutes of the International Telecommunication Union meetings (9% chose this)
The unit for potential difference between two points in a circuit is the
-
ampere (8% chose this)
-
volt (76% chose this)
-
ohm (6% chose this)
-
coulomb (10% chose this)
Parasitic oscillations in a RF power amplifier can be suppressed by
-
pulsing the supply voltage (4% chose this)
-
placing suitable chokes, ferrite beads or resistors within the amplifier (81% chose this)
-
screening all input leads (13% chose this)
-
using split-stator tuning capacitors (2% chose this)
A vertical antenna which uses a flat conductive surface at its base is the
-
vertical dipole (20% chose this)
-
quarter wave ground plane (78% chose this)
-
rhombic (2% chose this)
-
long wire (0% chose this)

In the block diagram shown, the connection between the SWR bridge and the antenna switch is normally a
-
twisted pair cable (7% chose this)
-
coaxial cable (88% chose this)
-
quarter-wave matching section (0% chose this)
-
short length of balanced ladder-line (5% chose this)
The frequency stability of a receiver is its ability to
-
stay tuned to the desired signal (90% chose this)
-
track the incoming signal as it drifts (5% chose this)
-
provide a frequency standard (5% chose this)
-
provide a digital readout (0% chose this)
Each stage of a three-stage amplifier provides 5 dB gain. The total amplification is
-
10 dB (4% chose this)
-
15 dB (76% chose this)
-
25 dB (4% chose this)
-
125 dB (16% chose this)
The speed of a radio wave
-
varies indirectly to the frequency (5% chose this)
-
is the same as the speed of light (86% chose this)
-
is infinite in space (2% chose this)
-
is always less than half the speed of light (7% chose this)
For your safety, before checking a fault in a mains operated power supply unit, first
-
short the leads of the filter capacitor (3% chose this)
-
turn off the power and remove the power plug (97% chose this)
-
check the action of the capacitor bleeder resistance (0% chose this)
-
remove and check the fuse in the power supply (0% chose this)
The correct instrument for measuring the supply current to an amplifier is a
-
wattmeter (7% chose this)
-
voltmeter (7% chose this)
-
ammeter (86% chose this)
-
ohmmeter (0% chose this)
A low-pass filter may be used in an amateur radio installation
-
to attenuate signals lower in frequency than the transmission (20% chose this)
-
to attenuate signals higher in frequency than the transmission (70% chose this)
-
to boost the output power of the lower frequency transmissions (7% chose this)
-
to boost the power of higher frequency transmissions (2% chose this)
The designed output impedance of the antenna socket of most modern transmitters is nominally
-
25 ohm (6% chose this)
-
50 ohm (76% chose this)
-
75 ohm (16% chose this)
-
100 ohm (2% chose this)
A transistor can be destroyed in a circuit by
-
excessive light (0% chose this)
-
excessive heat (90% chose this)
-
saturation (7% chose this)
-
cut-off (2% chose this)

In the block diagram shown, the "antenna switch"
-
switches the transmitter output to the dummy load for tune-up purposes (84% chose this)
-
switches the antenna from transmit to receive (0% chose this)
-
switches the frequency of the antenna for operation on different bands (2% chose this)
-
switches surplus output power from the antenna to the dummy load to avoid distortion. (13% chose this)
The figure in a receiver's specifications which indicates its sensitivity is the
-
bandwidth of the IF in kilohertz (13% chose this)
-
audio output in watts (4% chose this)
-
signal plus noise to noise ratio (83% chose this)
-
number of RF amplifiers (0% chose this)

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the "RF amplifier"
-
decreases random fluctuation noise (0% chose this)
-
is a restoring filter amplifier (0% chose this)
-
increases the incoming signal level (89% chose this)
-
changes the signal frequency (11% chose this)
The purpose of a balun in a transmitting antenna system is to
-
balance harmonic radiation (2% chose this)
-
reduce unbalanced standing waves (9% chose this)
-
protect the antenna system from lightning strikes (2% chose this)
-
match unbalanced and balanced transmission lines (87% chose this)
A General Amateur Operator Certificate of Competency is normally issued for
-
1 year (4% chose this)
-
5 years (2% chose this)
-
10 years (16% chose this)
-
life (78% chose this)
Many receivers have both RF and AF gain controls. These allow the operator to
-
vary the receiver frequency and AM transmitter frequency independently (2% chose this)
-
vary the low and high frequency audio gain independently (2% chose this)
-
vary the receiver's "real" and "absolute" frequencies independently (5% chose this)
-
vary the gain of the radio frequency and audio frequency amplifier stages independently (91% chose this)
The "S meter" on a receiver
-
indicates where the squelch control should be set (2% chose this)
-
indicates the standing wave ratio (15% chose this)
-
indicates the state of the battery voltage (0% chose this)
-
indicates relative incoming signal strengths (83% chose this)
The term "PTT" means
-
push to talk (98% chose this)
-
piezo-electric transducer transmitter (0% chose this)
-
phase testing terminal (0% chose this)
-
phased transmission transponder (3% chose this)
An amateur radio operator must be able to
-
converse in the languages shown on the Certificate of Competency (7% chose this)
-
read Morse code at 12 words-per-minute (0% chose this)
-
monitor standard frequency transmissions (2% chose this)
-
verify that transmissions are within an authorised frequency band (91% chose this)
A current of 0.5 ampere flows through a resistance when 6 volt is applied. To change the current to 0.25 ampere the voltage must be
-
increased to 12 volt (13% chose this)
-
reduced to 3 volt (85% chose this)
-
held constant (0% chose this)
-
reduced to zero (2% chose this)
Two 20 uH inductances are connected in series. The total inductance is
-
10 uH (14% chose this)
-
20 uH (4% chose this)
-
40 uH (80% chose this)
-
80 uH (2% chose this)
The voltage to cause a current of 4.4 ampere in a 50 ohm resistance is
-
2220 volt (0% chose this)
-
220 volt (87% chose this)
-
22.0 volt (9% chose this)
-
0.222 volt (4% chose this)
If two receivers are compared, the more sensitive receiver will produce
-
more than one signal (0% chose this)
-
less signal and more noise (7% chose this)
-
more signal and less noise (93% chose this)
-
a steady oscillator drift (0% chose this)
Three 12 ohm resistors are wired in parallel and connected to an 8 volt supply. The total current flow from the supply is
-
1 ampere (4% chose this)
-
2 amperes (75% chose this)
-
3 amperes (17% chose this)
-
4.5 amperes (4% chose this)
The name for the flow of electrons in an electric circuit is
-
voltage (13% chose this)
-
resistance (0% chose this)
-
capacitance (4% chose this)
-
current (83% chose this)
When a HF transmitted radio signal reaches a receiver, small changes in the ionosphere can cause
-
consistently stronger signals (2% chose this)
-
a change in the ground wave signal (2% chose this)
-
variations in signal strength (91% chose this)
-
consistently weaker signals (5% chose this)
The fifth harmonic of 7 MHz is
-
12 MHz (4% chose this)
-
19 MHz (6% chose this)
-
28 MHz (6% chose this)
-
35 MHz (83% chose this)
A switching system to use a single antenna for a separate transmitter and receiver should also
-
disable the unit not being used (74% chose this)
-
disconnect the antenna tuner (7% chose this)
-
ground the antenna on receive (17% chose this)
-
switch between power supplies (2% chose this)
The correct name for the equivalent of 'one cycle per second' is one
-
henry (0% chose this)
-
volt (0% chose this)
-
hertz (100% chose this)
-
coulomb (0% chose this)
The abbreviation �HF� refers to the radio spectrum between
-
2 MHz and 10 MHz (6% chose this)
-
3 MHz and 30 MHz (75% chose this)
-
20 MHz and 200 MHz (13% chose this)
-
30 MHz and 300 MHz (6% chose this)
Peak envelope power (PEP) output is the
-
average power output at the crest of the modulating cycle (70% chose this)
-
total power contained in each sideband (12% chose this)
-
carrier power output (7% chose this)
-
transmitter power output on key-up condition (11% chose this)
An important difference between a common torch battery and a lead acid battery is that only the lead acid battery
-
has two terminals (0% chose this)
-
contains an electrolyte (13% chose this)
-
can be re-charged (85% chose this)
-
can be effectively discharged (2% chose this)
Operation on the 130 to 190 kHz band requires
-
a vertical half-wave antenna (10% chose this)
-
special permission to operate in daylight hours (8% chose this)
-
power output limited to 5 watt e.i.r.p. maximum (77% chose this)
-
receivers with computers with sound cards (6% chose this)
A more important consideration when selecting an antenna for working stations at great distances is
-
sunspot activity (8% chose this)
-
angle of radiation (78% chose this)
-
impedance (8% chose this)
-
bandwidth (6% chose this)
A dry cell has an open circuit voltage of 1.5 volt. When supplying a large current the voltage drops to 1.2 volt. This is due to the cell's
-
internal resistance (80% chose this)
-
voltage capacity (6% chose this)
-
electrolyte becoming dry (4% chose this)
-
current capacity (10% chose this)
The frequency band 146 to 148 MHz is
-
shared with other communication services (74% chose this)
-
allocated exclusively for police communications (2% chose this)
-
exclusive to repeater operation (13% chose this)
-
reserved for emergency communications (11% chose this)
A low-pass filter is used in the antenna lead from a transmitter
-
to reduce key clicks developed in a CW transmitter (4% chose this)
-
to increase harmonic radiation (4% chose this)
-
to eliminate chirp in CW transmissions (4% chose this)
-
to reduce radiation of harmonics (87% chose this)
The unit of impedance is the
-
ampere (4% chose this)
-
farad (4% chose this)
-
henry (21% chose this)
-
ohm (71% chose this)
The total resistance in a parallel circuit
-
is always less than the smallest resistance (85% chose this)
-
depends upon the voltage drop across each branch (2% chose this)
-
could be equal to the resistance of one branch (13% chose this)
-
depends upon the applied voltage (0% chose this)
A current of 2 ampere flows through a 16 ohm resistance. The applied voltage is
-
8 volt (20% chose this)
-
14 volt (0% chose this)
-
18 volt (0% chose this)
-
32 volt (80% chose this)
The letters BBS stand for
-
binary baud system (14% chose this)
-
bulletin board system (78% chose this)
-
basic binary selector (2% chose this)
-
broadcast band stopper (6% chose this)
A New Zealand General Amateur Operator Certificate of Competency allows you to operate
-
anywhere in the world (9% chose this)
-
anywhere in New Zealand and in any other country that recognises the Certificate (91% chose this)
-
within 50 km of your home station location (0% chose this)
-
only at your home address (0% chose this)
The following phonetic code is correct for the callsign "ZL1AN"
-
zanzibar london one america norway (2% chose this)
-
zulu lima one alpha november (89% chose this)
-
zulu lima one able nancy (7% chose this)
-
zulu lima one able niner (2% chose this)
The following is a source of electrical energy
-
p-channel FET (0% chose this)
-
carbon resistor (2% chose this)
-
germanium diode (0% chose this)
-
lead acid battery (98% chose this)

In the transmitter block diagram shown, the "speech amplifier"
-
amplifies the audio signal from the microphone (84% chose this)
-
is a spectral equalization entropy changer (0% chose this)
-
amplifies only speech, while discriminating against background noises (14% chose this)
-
shifts the frequency spectrum of the audio signal into the RF region (2% chose this)
Three recognised layers of the ionosphere that affect radio propagation are
-
A, E, F (8% chose this)
-
B, D, E (6% chose this)
-
C, E, F (4% chose this)
-
D, E, F (82% chose this)
The resistor which gives the greatest opposition to current flow is
-
230 ohm (2% chose this)
-
1.2 kilohm (6% chose this)
-
1600 ohm (8% chose this)
-
0.5 megohm (84% chose this)
The following unit in a DC power supply performs a smoothing operation
-
an electrolytic capacitor (71% chose this)
-
a fuse (0% chose this)
-
a crowbar (5% chose this)
-
a full-wave diode bridge (24% chose this)
An amateur radio operator may knowingly interfere with another radio communication or signal
-
when the operator of another station is acting in an illegal manner (0% chose this)
-
when another station begins transmitting on a frequency you already occupy (0% chose this)
-
never (98% chose this)
-
when the interference is unavoidable because of crowded band conditions (2% chose this)
The output power rating of a linear amplifier in a SSB transmitter is specified by the
-
peak DC input power (6% chose this)
-
mean AC input power (0% chose this)
-
peak envelope power (85% chose this)
-
unmodulated carrier power (8% chose this)
Five 10 ohm resistors connected in series give a total resistance of
-
1 ohm (0% chose this)
-
5 ohms (0% chose this)
-
10 ohms (5% chose this)
-
50 ohms (95% chose this)

In the block diagram shown, the block designated "modem" is a
-
modulator/demodulator (91% chose this)
-
modulation emphasis unit (4% chose this)
-
Morse demodulator (0% chose this)
-
MOSFET de-emphasis unit (4% chose this)
The figures normally used in New Zealand amateur radio callsigns are
-
any two-digit number, 45 through 99 (18% chose this)
-
any two-digit number, 22 through 44 (5% chose this)
-
a single digit, 5 through 9 (11% chose this)
-
a single digit, 1 through 4 (66% chose this)
A harmonic of a signal transmitted at 3525 kHz would be expected to occur at
-
3573 kHz (10% chose this)
-
7050 kHz (85% chose this)
-
14025 kHz (2% chose this)
-
21050 kHz (2% chose this)
The MUF for a given radio path is the
-
mean of the maximum and minimum usable frequencies (2% chose this)
-
maximum usable frequency (85% chose this)
-
minimum usable frequency (10% chose this)
-
mandatory usable frequency (2% chose this)
Solar cycles have an average length of
-
1 year (10% chose this)
-
3 years (0% chose this)
-
6 years (6% chose this)
-
11 years (84% chose this)
The following can be adapted for use as a modem
-
an electronic keyer (2% chose this)
-
a spare transceiver (10% chose this)
-
a spare receiver (4% chose this)
-
a computer sound-card (84% chose this)
The purpose of a VOX unit in a transceiver is to
-
change from receiving to transmitting using the sound of the operator's voice (85% chose this)
-
check the transmitting frequency using the voice operated crystal (2% chose this)
-
enable a volume operated extension speaker for remote listening (10% chose this)
-
enable the variable oscillator crystal (2% chose this)
A low-pass filter for a high frequency transmitter output would
-
attenuate frequencies above 30 MHz (75% chose this)
-
pass audio frequencies below 3 kHz (9% chose this)
-
attenuate frequencies below 30 MHz (15% chose this)
-
pass audio frequencies above 3 kHz (2% chose this)
Skip distance is a term associated with signals through the ionosphere. Skip effects are due to
-
reflection and refraction from the ionosphere (95% chose this)
-
selective fading of local signals (0% chose this)
-
high gain antennas being used (2% chose this)
-
local cloud cover (2% chose this)
If an antenna feedline must pass near grounded metal objects, the following type should be used
-
75 ohm twinlead (4% chose this)
-
300 ohm twinlead (2% chose this)
-
600 ohm open-wire (4% chose this)
-
coaxial cable (89% chose this)
A band-pass filter will
-
pass frequencies each side of a band (18% chose this)
-
attenuate low frequencies but not high frequencies (2% chose this)
-
attenuate frequencies each side of a band (75% chose this)
-
attenuate high frequencies but not low frequencies (5% chose this)
Your responsibility as a station operator is that you must
-
allow another amateur to operate your station upon request (4% chose this)
-
be present whenever the station is operated (10% chose this)
-
be responsible for the proper operation of the station in accordance with the Radiocommunications Regulations (85% chose this)
-
notify the Ministry of Business, Innovation, and Employment if another amateur acts as the operator (0% chose this)
A receiver squelch circuit
-
automatically keeps the audio output at maximum level (0% chose this)
-
silences the receiver speaker during periods of no received signal (95% chose this)
-
provides a noisy operating environment (5% chose this)
-
is not suitable for pocket-size receivers (0% chose this)
A Yagi antenna is said to have a power gain over a dipole antenna for the same frequency band because
-
it radiates more power than a dipole (2% chose this)
-
more powerful transmitters can use it (2% chose this)
-
it concentrates the radiation in one direction (93% chose this)
-
it can be used for more than one band (2% chose this)
The accepted way to announce that you are listening to a VHF repeater is
-
"hello 6695, this is ZL2ZZZ listening" (10% chose this)
-
"calling 6695, 6695, 6695 from ZL2ZZZ" (0% chose this)
-
"6695 from ZL2ZZZ" (6% chose this)
-
"ZL2ZZZ listening on 6695" (84% chose this)
The sensitivity of a receiver specifies
-
the bandwidth of the RF preamplifier (2% chose this)
-
the stability of the oscillator (6% chose this)
-
its ability to receive weak signals (89% chose this)
-
its ability to reject strong signals (2% chose this)
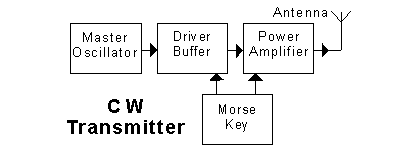
In the transmitter block diagram shown, the "master oscillator" produces
-
a steady signal at the required carrier frequency (79% chose this)
-
a pulsating signal at the required carrier frequency (11% chose this)
-
a 800 Hz signal to modulate the carrier (8% chose this)
-
a modulated CW signal (2% chose this)
An amplifier with a gain of 20 dB has a -10 dB attenuator connected in cascade. The gain of the combination is
-
8 dB (4% chose this)
-
10 dB (86% chose this)
-
-10 dB (4% chose this)
-
-200 dB (6% chose this)
The 'skywave' is another name for the
-
ionospheric wave (95% chose this)
-
tropospheric wave (5% chose this)
-
ground wave (0% chose this)
-
inverted wave (0% chose this)
Signal fadeouts resulting from an 'ionospheric storm' or 'sudden ionospheric disturbance' are usually attributed to
-
heating of the ionised layers (9% chose this)
-
over-use of the signal path (0% chose this)
-
insufficient transmitted power (2% chose this)
-
solar flare activity (89% chose this)
The better conductor of electricity is
-
copper (95% chose this)
-
carbon (0% chose this)
-
silicon (2% chose this)
-
aluminium (2% chose this)
The callsign of a New Zealand amateur radio station
-
is listed in the administration's database (86% chose this)
-
can be any sequence of characters made-up by the operator (2% chose this)
-
can never be changed (12% chose this)
-
is changed annually (0% chose this)
The purpose of the final amplifier in a transmitter is to
-
increase the frequency of a signal (2% chose this)
-
isolate the multiplier and later stages (0% chose this)
-
produce a stable radio frequency (12% chose this)
-
increase the power fed to the antenna (86% chose this)
I = E/R is a mathematical equation describing
-
Ohm's Law (98% chose this)
-
Thevenin's Theorem (0% chose this)
-
Kirchoff's First Law (2% chose this)
-
Kirchoff's Second Law (0% chose this)
The ionosphere
-
is a magnetised belt around the earth (2% chose this)
-
consists of magnetised particles around the earth (0% chose this)
-
is formed from layers of ionised gases around the earth (91% chose this)
-
is a spherical belt of solar radiation around the earth (6% chose this)

The block marked 'Rectifier' in the diagram is to
-
turn the AC voltage from the transformer into a fluctuating DC voltage (74% chose this)
-
rectify any waveform errors introduced by the transformer (7% chose this)
-
turn the sinewave output of the rectifier into a square wave (2% chose this)
-
smooth the DC waveform (17% chose this)
The purpose of using three wires in the mains power cord and plug on amateur radio equipment is to
-
make it inconvenient to use (0% chose this)
-
prevent the chassis from becoming live in case of an internal short to the chassis (93% chose this)
-
prevent the plug from being reversed in the wall outlet (0% chose this)
-
prevent short circuits (7% chose this)
Your General Amateur Operator Certificate of Competency permits you to
-
work citizen band stations (8% chose this)
-
establish and operate an earth station in the amateur satellite service (90% chose this)
-
service commercial radio equipment over 1 kW output (2% chose this)
-
re-wire fixed household electrical supply mains (0% chose this)
Before explaining to a neighbour that the reported interference is due to a lack of immunity in the neighbour's electronic equipment
-
disconnect all your equipment from their power sources (2% chose this)
-
write a letter to the MBIE (0% chose this)
-
make sure that there is no interference on your own domestic equipment (98% chose this)
-
ignore all complaints and take no action (0% chose this)
The number of high frequency bands open to long distance communication at any time depends on
-
the highest frequency at which ionospheric reflection can occur (93% chose this)
-
the number of frequencies the receiver can tune (2% chose this)
-
the power being radiated by the transmitting station (0% chose this)
-
the height of the transmitting antenna (4% chose this)
The signal from a CW transmitter consists of
-
a continuous, unmodulated RF waveform (9% chose this)
-
a continuous RF waveform modulated with an 800 Hz Morse signal (6% chose this)
-
an RF waveform which is keyed on and off to form Morse characters (81% chose this)
-
a continuous RF waveform which changes frequency in synchronism with an applied Morse signal (4% chose this)
The voltage across a resistor carrying current can be calculated using the formula
-
E = I + R [voltage equals current plus resistance] (4% chose this)
-
E = I - R [voltage equals current minus resistance] (0% chose this)
-
E = I x R [voltage equals current times resistance] (88% chose this)
-
E = I / R [voltage equals current divided by resistance] (8% chose this)
One GHz is equal to
-
1000 kHz (6% chose this)
-
10 MHz (2% chose this)
-
100 MHz (0% chose this)
-
1000 MHz (91% chose this)
You are mobile and talking through a VHF repeater. The other station reports that you keep "dropping out". This means
-
your signal is drifting lower in frequency (12% chose this)
-
your signal does not have enough strength to operate the repeater (86% chose this)
-
your voice is too low-pitched to be understood (2% chose this)
-
you are not speaking loudly enough (0% chose this)
The current flowing through a resistor can be calculated by using the formula
-
I = E x R [current equals voltage times resistance] (14% chose this)
-
I = E / R [current equals voltage divided by resistance] (86% chose this)
-
I = E + R [current equals voltage plus resistance] (0% chose this)
-
I = E - R [current equals voltage minus resistance] (0% chose this)
You may operate your amateur radio station somewhere in New Zealand for short periods away from the location entered in the administration's database
-
only during times of emergency (0% chose this)
-
only after giving proper notice to the Ministry of Business, Innovation, and Employment (8% chose this)
-
during an approved emergency practice (2% chose this)
-
whenever you want to (90% chose this)
An amateur station may transmit unidentified signals
-
when making a brief test not intended for reception by anyone else (13% chose this)
-
when conducted on a clear frequency when no interference will be caused (4% chose this)
-
when the meaning of transmitted information must be obscured to preserve secrecy (0% chose this)
-
never, such transmissions are not permitted (83% chose this)
The abbreviation �VHF� refers to the radio spectrum between
-
2 MHz and 10 MHz (0% chose this)
-
3 MHz and 30 MHz (11% chose this)
-
30 MHz and 300 MHz (83% chose this)
-
200 MHz and 2000 MHz (6% chose this)
Unwanted signals from a radio transmitter which cause harmful interference to other users are known as
-
rectified signals (2% chose this)
-
re-radiation signals (2% chose this)
-
reflected signals (2% chose this)
-
harmonic and other spurious signals (94% chose this)
The correct phonetic code for the callsign VK5ZX is
-
victor kilowatt five zulu xray (6% chose this)
-
victor kilo five zulu xray (90% chose this)
-
victor kilo five zanzibar xray (2% chose this)
-
victoria kilo five zulu xray (2% chose this)
A 5 ohm and a 10 ohm resistor are wired in series and connected to a 15 volt power supply. The current flowing from the power supply is
-
0.5 ampere (6% chose this)
-
1 ampere (83% chose this)
-
2 ampere (4% chose this)
-
15 ampere (8% chose this)
The type of atmospheric layers which will best return signals to earth are
-
oxidised layers (0% chose this)
-
heavy cloud layers (2% chose this)
-
ionised layers (94% chose this)
-
sun spot layers (4% chose this)
All amateur stations, regardless of the mode of transmission used, must be equipped with
-
a reliable means for determining the operating radio frequency (100% chose this)
-
a dummy antenna (0% chose this)
-
an overmodulation indicating device (0% chose this)
-
a dc power meter (0% chose this)
The medium which reflects high frequency radio waves back to the earth's surface is called the
-
biosphere (2% chose this)
-
stratosphere (2% chose this)
-
ionosphere (88% chose this)
-
troposphere (8% chose this)
Morse code is permitted for use by
-
only operators who have passed a Morse code test (4% chose this)
-
those stations with computers to decode it (0% chose this)
-
any amateur radio operator (96% chose this)
-
only those stations equipped for headphone reception (0% chose this)

In the transmitter block diagram shown, the "VFO" is
-
a voice frequency oscillator (12% chose this)
-
a varactor fixed oscillator (4% chose this)
-
a virtual faze oscillator (0% chose this)
-
a variable frequency oscillator (85% chose this)
A General Amateur Operator Certificate of Competency can be inspected by an authorised officer from the Ministry of Business, Innovation, and Employment
-
at any time (88% chose this)
-
on any business day (12% chose this)
-
before 9 p.m. (0% chose this)
-
only on public holidays (0% chose this)
The ability of a receiver to separate signals close in frequency is called its
-
noise figure (2% chose this)
-
sensitivity (15% chose this)
-
bandwidth (0% chose this)
-
selectivity (83% chose this)
The "split frequency" function on a transceiver allows the operator to
-
transmit on one frequency and receive on another (86% chose this)
-
monitor two frequencies simultaneously using a single loudspeaker (8% chose this)
-
monitor two frequencies simultaneously using two loudspeakers (4% chose this)
-
receive CW and SSB signals simultaneously on the same frequency (2% chose this)
The substance which will most readily allow an electric current to flow is
-
an insulator (2% chose this)
-
a conductor (94% chose this)
-
a resistor (2% chose this)
-
a dielectric (2% chose this)
The organisation responsible for the International Radio Regulations is the
-
European Radiocommunications Office (2% chose this)
-
United Nations (0% chose this)
-
International Telecommunication Union (98% chose this)
-
European Telecommunication Standards Institute (0% chose this)
Electromagnetic compatibility is
-
two antennas facing each other (4% chose this)
-
the ability of equipment to function satisfactorily in its own environment without introducing intolerable electromagnetic disturbances (88% chose this)
-
more than one relay solenoid operating simultaneously (2% chose this)
-
the inability of equipment to function satisfactorily together and produce tolerable electromagnetic disturbances (6% chose this)
If you hear distress traffic and are unable to render assistance, you should
-
maintain watch until you are certain that assistance is forthcoming (94% chose this)
-
enter the details in the log book and take no further action (0% chose this)
-
take no action (0% chose this)
-
tell all other stations to cease transmitting (6% chose this)
One way to operate a 3 volt bulb from a 9 volt supply is to connect it in
-
series with the supply (2% chose this)
-
parallel with the supply (8% chose this)
-
series with a resistor (87% chose this)
-
parallel with a resistor (4% chose this)
Two 120 ohm resistors are arranged in parallel to replace a faulty resistor. The faulty resistor had an original value of
-
15 ohm (2% chose this)
-
30 ohm (8% chose this)
-
60 ohm (85% chose this)
-
120 ohm (6% chose this)
Four good electrical insulators are
-
plastic, rubber, wood, carbon (8% chose this)
-
glass, wood, copper, porcelain (2% chose this)
-
paper, glass, air, aluminium (4% chose this)
-
glass, air, plastic, porcelain (87% chose this)
When an 8 ohm resistor is connected across a 12 volt supply the current flow is
-
12 / 8 amps (88% chose this)
-
8 / 12 amps (6% chose this)
-
12 - 8 amps (6% chose this)
-
12 + 8 amps (0% chose this)
A log-book for recording stations worked
-
is compulsory for every amateur radio operator (18% chose this)
-
is recommended for all amateur radio operators (80% chose this)
-
must list all messages sent (0% chose this)
-
must record time in UTC (2% chose this)
The Amateur Service may be briefly defined as
-
a private radio service for personal gain and public benefit (0% chose this)
-
a public radio service used for public service communications (2% chose this)
-
a radiocommunication service for the purpose of self-training, intercommunication and technical investigation (96% chose this)
-
a private radio service intended only for emergency communications (2% chose this)
The unit for power is the
-
ohm (0% chose this)
-
watt (96% chose this)
-
ampere (2% chose this)
-
volt (2% chose this)
After qualifying and gaining a General Amateur Operator Certificate of Competency you are permitted to
-
operate on any frequency in the entire radio spectrum (2% chose this)
-
first operate for three months on amateur radio bands below 5 MHz and bands above 25 MHz to log fifty or more contacts (94% chose this)
-
ignore published bandplans (2% chose this)
-
make frequent tune-up transmissions at 10 MHz (2% chose this)
An RF transmission line should be matched at the transmitter end to
-
prevent frequency drift (0% chose this)
-
overcome fading of the transmitted signal (2% chose this)
-
ensure that the radiated signal has the intended polarisation (4% chose this)
-
transfer maximum power to the antenna (94% chose this)
A simple transmitter requires a 50 ohm dummy load. You can fabricate this from
-
four 300 ohm resistors in parallel (8% chose this)
-
five 300 ohm resistors in parallel (4% chose this)
-
six 300 ohm resistors in parallel (87% chose this)
-
seven 300 ohm resistors in parallel (2% chose this)
VHF or UHF signals transmitted towards a tall building are often received at a more distant point in another direction because
-
these waves are easily bent by the ionosphere (0% chose this)
-
these waves are easily reflected by objects in their path (100% chose this)
-
you can never tell in which direction a wave is travelling (0% chose this)
-
tall buildings have elevators (0% chose this)
The abbreviation AGC means
-
attenuating gain capacitor (4% chose this)
-
automatic gain control (94% chose this)
-
anode-grid capacitor (2% chose this)
-
amplified grid conductance (0% chose this)
The ohm is the unit of
-
supply voltage (0% chose this)
-
electrical pressure (0% chose this)
-
current flow (10% chose this)
-
electrical resistance (90% chose this)
An ammeter should not be connected directly across the terminals of a 12 volt car battery because
-
the resulting high current will probably destroy the ammeter (87% chose this)
-
no current will flow because no other components are in the circuit (11% chose this)
-
the battery voltage will be too low for a measurable current to flow (0% chose this)
-
the battery voltage will be too high for a measurable current to flow (2% chose this)
One megahertz is equal to
-
0.0001 Hz (0% chose this)
-
100 kHz (0% chose this)
-
1000 kHz (98% chose this)
-
10 Hz (2% chose this)
An impure signal is found to have 2 kHz and 4 kHz components. This 4 kHz signal is
-
a fundamental of the 2 kHz signal (4% chose this)
-
a sub-harmonic of 2 kHz (2% chose this)
-
the DC component of the main signal (0% chose this)
-
a harmonic of the 2 kHz signal (94% chose this)
To obtain efficient transfer of power from a transmitter to an antenna, it is important that there is a
-
high load impedance (0% chose this)
-
low load impedance (4% chose this)
-
correct impedance match between transmitter and antenna (92% chose this)
-
high standing wave ratio (4% chose this)
If the qualified operator of an amateur radio station is absent overseas, the home station may be used by
-
any member of the immediate family to maintain contact with only the qualified operator (0% chose this)
-
any person with an appropriate General Amateur Operator Certificate of Competency (96% chose this)
-
the immediate family to communicate with any amateur radio operator (2% chose this)
-
the immediate family if a separate callsign for mobile use has been obtained by the absent operator (2% chose this)
High Frequency long-distance propagation is most dependent on
-
ionospheric reflection (92% chose this)
-
tropospheric reflection (6% chose this)
-
ground reflection (2% chose this)
-
inverted reflection (0% chose this)
One kilohm is
-
10 ohm (0% chose this)
-
0.01 ohm (0% chose this)
-
0.001 ohm (4% chose this)
-
1000 ohm (96% chose this)
Two 100 ohm resistors connected in parallel are wired in series with a 10 ohm resistor. The total resistance of the combination is
-
60 ohms (87% chose this)
-
180 ohms (4% chose this)
-
190 ohms (2% chose this)
-
210 ohms (8% chose this)
An element which falls somewhere between being an insulator and a conductor is called a
-
P-type conductor (2% chose this)
-
intrinsic conductor (6% chose this)
-
semiconductor (90% chose this)
-
N-type conductor (2% chose this)
As a New Zealand amateur radio operator you
-
must regularly operate using dry batteries (2% chose this)
-
should use shortened antennas (0% chose this)
-
may train for and support disaster relief activities (98% chose this)
-
must always have solar-powered equipment in reserve (0% chose this)
The following two quantities should be multiplied together to find power
-
resistance and capacitance (0% chose this)
-
voltage and current (94% chose this)
-
voltage and inductance (6% chose this)
-
inductance and capacitance (0% chose this)
Resistors of 10, 270, 3900, and 100 ohm are connected in series. The total resistance is
-
9 ohm (0% chose this)
-
3900 ohm (2% chose this)
-
4280 ohm (98% chose this)
-
10 ohm (0% chose this)
The skip distance of radio signals is determined by the
-
type of transmitting antenna used (0% chose this)
-
power fed to the final amplifier of the transmitter (0% chose this)
-
only the angle of radiation from the antenna (4% chose this)
-
both the height of the ionosphere and the angle of radiation from the antenna (96% chose this)
You identify your amateur station by transmitting your
-
"handle" (0% chose this)
-
callsign (100% chose this)
-
first name and your location (0% chose this)
-
full name (0% chose this)
A dummy antenna
-
attenuates a signal generator to a desirable level (0% chose this)
-
provides more selectivity when a transmitter is being tuned (6% chose this)
-
matches an AF generator to the receiver (0% chose this)
-
duplicates the characteristics of an antenna without radiating signals (94% chose this)
The watt is the unit of
-
power (100% chose this)
-
magnetic flux (0% chose this)
-
electromagnetic field strength (0% chose this)
-
breakdown voltage (0% chose this)
Bandplans showing the transmission modes for New Zealand amateur radio bands are developed and published for the mutual respect and advantage of all operators
-
to ensure that your operations do not impose problems on other operators and that their operations do not impact on you (100% chose this)
-
to keep experimental developments contained (0% chose this)
-
to reduce the number of modes in any one band (0% chose this)
-
to keep overseas stations separate from local stations (0% chose this)
Increasing the number of turns on an inductor will make its inductance
-
decrease (8% chose this)
-
increase (92% chose this)
-
remain unchanged (0% chose this)
-
become resistive (0% chose this)
Before calling CQ on the HF bands, you should
-
listen first, then ask if the frequency is in use (98% chose this)
-
request that other operators clear the frequency (0% chose this)
-
request a signal report from any station listening (2% chose this)
-
use a frequency where many stations are already calling (0% chose this)

In the block diagram shown, the connection between the "antenna tuner" and the "antenna" could be made with
-
three-wire mains power cable (2% chose this)
-
heavy hook-up wire (4% chose this)
-
50 ohm coaxial cable (92% chose this)
-
an iron-cored transformer (2% chose this)
The following two electrical units multiplied together give the unit "watt"
-
volt and ampere (98% chose this)
-
volt and farad (2% chose this)
-
farad and henry (0% chose this)
-
ampere and henry (0% chose this)
The following unit in a DC power supply performs a rectifying operation
-
an electrolytic capacitor (20% chose this)
-
a fuse (3% chose this)
-
a crowbar (7% chose this)
-
a full-wave diode bridge (70% chose this)
The transmitter power output for amateur stations at all times is
-
25 watt PEP minimum output (0% chose this)
-
that needed to overcome interference from other stations (2% chose this)
-
1000 watt PEP maximum (6% chose this)
-
the minimum power necessary to communicate and within the terms of the amateur radio GURL (92% chose this)
The following material is considered to be a semiconductor
-
copper (6% chose this)
-
sulphur (0% chose this)
-
silicon (94% chose this)
-
tantalum (0% chose this)
Unqualified persons in your family cannot transmit using your amateur station if they are alone with your equipment because they must
-
not use your equipment without your permission (0% chose this)
-
hold a General Amateur Operator Certificate of Competency before they are allowed to be operators (100% chose this)
-
first know how to use the right abbreviations and Q signals (0% chose this)
-
first know the right frequencies and emissions for transmitting (0% chose this)
A "pileup" is
-
an old, worn-out radio (0% chose this)
-
another name for a junkbox (0% chose this)
-
a large group of stations all calling the same DX station (98% chose this)
-
a type of selenium rectifier (2% chose this)
A current of 5 ampere in a 50 ohm resistance produces a potential difference of
-
20 volt (13% chose this)
-
45 volt (0% chose this)
-
55 volt (2% chose this)
-
250 volt (86% chose this)

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the waveform produced by the "oscillator" would ideally be a
-
square wave (2% chose this)
-
pulsed wave (0% chose this)
-
sinewave (94% chose this)
-
hybrid frequency wave (4% chose this)
Before operating an amateur station in a motor vehicle, you must
-
give the Land Transport Authority the vehicle's licence plate number (8% chose this)
-
inform the Ministry of Business, Innovation, and Employment (0% chose this)
-
hold a current General Amateur Operator Certificate of Competency (92% chose this)
-
obtain an additional callsign (0% chose this)
These letters are generally used for the first letters in New Zealand amateur radio callsigns
-
ZS (2% chose this)
-
ZL (94% chose this)
-
VK (4% chose this)
-
LZ (0% chose this)
One mA is
-
one millionth of one ampere (15% chose this)
-
one thousandth of one ampere (83% chose this)
-
one tenth of one ampere (2% chose this)
-
one millionth of admittance (0% chose this)
"VOX" stands for
-
volume operated extension speaker (2% chose this)
-
voice operated transmit (91% chose this)
-
variable oscillator transmitter (0% chose this)
-
voice operated expander (7% chose this)
International communications on behalf of third parties may be transmitted by an amateur station only if
-
prior remuneration has been received (0% chose this)
-
such communications have been authorised by the countries concerned (91% chose this)
-
the communication is transmitted in secret code (2% chose this)
-
English is used to identify the station at the end of each transmission (7% chose this)
In digital communications, FSK stands for
-
phase selection keying (2% chose this)
-
final section keying (0% chose this)
-
frequency shift keying (98% chose this)
-
final signal keying (0% chose this)
Six identical 2-volt bulbs are connected in series. The supply voltage to cause the bulbs to light normally is
-
12 V (91% chose this)
-
1.2 V (0% chose this)
-
6 V (2% chose this)
-
2 V (7% chose this)

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the "AF amplifier"
-
rejects AM and RTTY signals (0% chose this)
-
amplifies audio frequency signals (94% chose this)
-
has a very narrow passband (6% chose this)
-
restores ambiance to the audio (0% chose this)
You must have a General Amateur Operator Certificate of Competency to
-
transmit on public-service frequencies (4% chose this)
-
retransmit shortwave broadcasts (2% chose this)
-
repair radio equipment (0% chose this)
-
transmit in bands allocated to the Amateur Service (94% chose this)
This callsign could be allocated to an amateur radio operator in New Zealand
-
ZK-CKF (2% chose this)
-
ZLC5 (5% chose this)
-
ZL2HF (91% chose this)
-
ZMX4432 (2% chose this)
The age when an amateur radio operator is required to surrender the General Amateur Operator Certificate of Competency is
-
65 years (0% chose this)
-
70 years (0% chose this)
-
75 years (0% chose this)
-
there is no age limit (100% chose this)
The Morse code signal SOS is sent by a station
-
with an urgent message (0% chose this)
-
in grave and imminent danger and requiring immediate assistance (100% chose this)
-
making a report about a shipping hazard (0% chose this)
-
sending important weather information (0% chose this)
A coaxial feedline is constructed from
-
a single conductor (4% chose this)
-
two parallel conductors separated by spacers (2% chose this)
-
braid and insulation around a central conductor (91% chose this)
-
braid and insulation twisted together (4% chose this)
The main characteristic of a vertical antenna is that it
-
requires few insulators (2% chose this)
-
is very sensitive to signals coming from horizontal aerials (5% chose this)
-
receives signals from all points around it equally well (93% chose this)
-
is easy to feed with TV ribbon feeder (0% chose this)
These magnetic poles repel
-
unlike (7% chose this)
-
like (89% chose this)
-
positive (2% chose this)
-
negative (2% chose this)
You must keep the following document at your amateur station
-
your General Amateur Operator Certificate of Competency (100% chose this)
-
a copy of the Rules and Regulations for the Amateur Service (0% chose this)
-
a copy of the Radio Amateur's Handbook for instant reference (0% chose this)
-
a chart showing the amateur radio bands (0% chose this)
An Amateur Station is one which is
-
operated by the holder of a General Amateur Operator Certificate of Competency on the amateur radio bands (91% chose this)
-
owned and operated by a person who is not engaged professionally in radio communications (7% chose this)
-
used exclusively to provide two-way communication in connection with activities of amateur sporting organisations (0% chose this)
-
used primarily for emergency communications during floods, earthquakes and similar disasters. (2% chose this)
An Amateur Station is a station
-
in the public radio service (2% chose this)
-
using radiocommunications for a commercial purpose (2% chose this)
-
using equipment for training new radiocommunications operators (5% chose this)
-
in the Amateur Service (91% chose this)
You can safely remove an unconscious person from contact with a high voltage source by
-
pulling an arm or a leg (0% chose this)
-
wrapping the person in a blanket and pulling to a safe area (4% chose this)
-
calling an electrician (0% chose this)
-
turning off the high voltage and then removing the person (96% chose this)
As a New Zealand amateur radio operator you may communicate with
-
only amateur stations within New Zealand (2% chose this)
-
only stations running more than 500w PEP output (2% chose this)
-
only stations using the same transmission mode (4% chose this)
-
other amateur stations world-wide (93% chose this)

In the transmitter block diagram shown, the "linear amplifier"
-
has all components arranged in-line (0% chose this)
-
amplifies the modulated signal with no distortion (93% chose this)
-
aligns the two sidebands correctly (0% chose this)
-
removes any unwanted amplitude modulation from the signal (7% chose this)
A person in distress
-
must use correct communication procedures (0% chose this)
-
may use any means available to attract attention (95% chose this)
-
must give position with a grid reference (4% chose this)
-
must use allocated safety frequencies (2% chose this)
A 50 hertz current in a wire means that
-
a potential difference of 50 volts exists across the wire (0% chose this)
-
the current flowing in the wire is 50 amperes (0% chose this)
-
the power dissipated in the wire is 50 watts (0% chose this)
-
a cycle is completed 50 times in each second (100% chose this)
The plastic coating formed around wire is
-
an insulator (98% chose this)
-
a conductor (2% chose this)
-
an inductor (0% chose this)
-
a magnet (0% chose this)
This rule applies if two amateur radio stations want to use the same frequency
-
the operator with the newer qualification must yield the frequency to the more experienced operator (2% chose this)
-
the station with the lower power output must yield the frequency to the station with the higher power output (2% chose this)
-
both stations have an equal right to operate on the frequency, the second-comer courteously giving way after checking that the frequency is in use (96% chose this)
-
stations in ITU Regions 1 and 2 must yield the frequency to stations in Region 3 (0% chose this)
An amateur station may be closed down at any time by
-
a demand from an irate neighbour experiencing television interference (0% chose this)
-
a demand from an authorised official of the Ministry of Business, Innovation, and Employment (96% chose this)
-
an official from your local council (4% chose this)
-
anyone until your aerials are made less unsightly (0% chose this)
An electrical insulator
-
lets electricity flow through it in one direction (0% chose this)
-
does not let electricity flow through it (98% chose this)
-
lets electricity flow through it when light shines on it (0% chose this)
-
lets electricity flow through it (2% chose this)
The term "harmful interference" means
-
interference which obstructs or repeatedly interrupts radiocommunication services (92% chose this)
-
an antenna system which accidentally falls on to a neighbour's property (0% chose this)
-
a receiver with the audio volume unacceptably loud (0% chose this)
-
interference caused by a station of a secondary service (8% chose this)
Messages from an amateur station in one of the following are expressly forbidden
-
ASCII (2% chose this)
-
International No. 2 code (0% chose this)
-
Baudot code (2% chose this)
-
secret cipher (96% chose this)
When interference to the reception of radiocommunications is caused by the operation of an amateur station, the station operator
-
must immediately comply with any action required by the Ministry of Business, Innovation, and Employment to prevent the interference (93% chose this)
-
may continue to operate with steps taken to reduce the interference when the station operator can afford it (3% chose this)
-
may continue to operate without restrictions (0% chose this)
-
is not obligated to take any action (3% chose this)
When someone in the neighbourhood complains of TVI it is wise to
-
deny all responsibility (0% chose this)
-
immediately blame the other equipment (0% chose this)
-
inform all the other neighbours (2% chose this)
-
check your log to see if it coincides with your transmissions (98% chose this)
When living in a densely-populated area, it is wise to
-
always use maximum transmitter output power (2% chose this)
-
use the minimum transmitter output power necessary (97% chose this)
-
only transmit during popular television programme times (0% chose this)
-
point the beam at the maximum number of television antennas (2% chose this)
A General Amateur Operator Certificate of Competency
-
can never be revoked (0% chose this)
-
gives a waiver over copyright (2% chose this)
-
does not confer on its holder a monopoly on the use of any frequency or band (98% chose this)
-
can be readily transferred (0% chose this)
The following could power a solid-state 10 watt VHF transceiver
-
a 12 volt car battery (88% chose this)
-
6 penlite cells in series (3% chose this)
-
a 12 volt, 500 mA plug-pack (2% chose this)
-
a 6 volt 10 Amp-hour Gel cell. (8% chose this)
A mains operated DC power supply
-
converts DC from the mains into AC of the same voltage (4% chose this)
-
converts energy from the mains into DC for operating electronic equipment (96% chose this)
-
is a diode-capacitor device for measuring mains power (0% chose this)
-
is a diode-choked device for measuring inductance power (0% chose this)
HamStudy.org™ is copyright 2026 Signal Stuff™, All rights
reserved.
View Privacy Policy | Get help with HamStudy.org™
View Privacy Policy | Get help with HamStudy.org™
