ELECTRONIC AND ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
Fixed and variable resistors; Capacitors; Inductors; Fuses; Switches; Batteries
What electrical component opposes the flow of current in a DC circuit?
-
Inductor
-
Correct AnswerResistor
-
Inverter
-
Transformer
A resistor is the component that opposes the flow of current in a DC circuit. It does this by converting electrical energy into heat, and the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance is given by Ohm's law (V = I·R). For a fixed voltage, a larger resistance results in a smaller current.
An inductor does not oppose steady DC current; it resists changes in current (for example, in AC or during transients) but once DC is steady an ideal inductor behaves like a short circuit.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Resistor
Memory aids:
- Think of the word "resist" in resistor — to oppose
- Remember: inductors oppose changes in current, not steady DC
Last edited by zorba. Register to edit
Tags: none
What type of component is often used as an adjustable volume control?
-
Fixed resistor
-
Power resistor
-
Correct AnswerPotentiometer
-
Transformer
A potentiometer (pot) is commonly used as an adjustable volume control because it can be configured as a user‑controlled variable resistor or as a voltage divider. By changing the resistance or the fraction of the input voltage that is passed on, the pot changes the amplitude of the audio signal sent to the amplifier or speaker, which adjusts the perceived loudness.
A potentiometer has three parts: a resistive track (made of carbon, conductive plastic, or similar material), a metal wiper that slides along the track, and three terminals (the two ends of the track and the wiper). Moving the wiper changes the resistance seen by the circuit or the voltage at the wiper terminal, and that change in voltage/resistance is what varies the volume.
Last edited by godfreyhom. Register to edit
Tags: none
What electrical parameter is controlled by a potentiometer?
-
Inductance
-
Correct AnswerResistance
-
Capacitance
-
Field strength
A potentiometer is a variable resistor. Its schematic symbol looks like a resistor with an arrow (the wiper) pointing to the middle of the resistor element. Potentiometers commonly have three terminals: the two outer terminals are the ends of the resistive element (the total resistance between them) and the middle terminal is the movable wiper. As the wiper is moved, the resistance between the wiper and each end changes—one side increases while the other decreases—so the device is used to control resistance (and can also be used as an adjustable voltage divider).
For more detail see: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Potentiometer
Memory aids:
- "You’d want to resist(ance) any potent(iometer) food."
Last edited by afton.shearer@gmail.com. Register to edit
Tags: none
What electrical component stores energy in an electric field?
-
Resistor
-
Correct AnswerCapacitor
-
Inductor
-
Diode
There are two questions in the pool that are very similar; one asks about a component storing energy in an electric field, the other in a magnetic field. The electric field is a capacitor; it consists of at least two conductors separated by an insulator (or dielectric). When voltage is applied to the capacitor it will initially pull a lot of current, dropping the voltage and slowly charging up an electric field (due to the difference in potential between the positive and negative charges on the capacitor). Capacitors thus store energy in the electric field, and once they have charged up they no longer allow current to pass through.
If the power source (such as a battery) is removed, the capacitor will begin to discharge, initially keeping the circuit at exactly the same voltage as before with the current dying down until the voltage can no longer be maintained with the energy remaining in the electric field. For this reason, we say that a capacitor resists change in voltage.
Memory aids:
- "MICE:" (M)agnetic field — (I)nductor. (C)apacitor — (E)lectric field.
Last edited by ki5bzz. Register to edit
Tags: none
What type of electrical component consists of conductive surfaces separated by an insulator?
-
Resistor
-
Potentiometer
-
Oscillator
-
Correct AnswerCapacitor
A capacitor is an electrical component that stores energy in an electric field. It consists of at least two conductive surfaces (plates) separated by an insulator (called a dielectric). When voltage is applied to the capacitor, charge accumulates on the plates, creating an electric field between them and storing energy.
The schematic symbol for a capacitor resembles its physical construction: two parallel lines (plates) separated by a gap.
When first connected to a voltage source, a capacitor will draw current as it charges; as the voltage across the capacitor approaches the source voltage, the charging current falls off and the capacitor no longer allows steady current to pass through (it blocks DC once fully charged). If the voltage source is removed, the capacitor will discharge, supplying current until the stored energy in the electric field is depleted. Because a capacitor opposes rapid changes in voltage across its terminals, it is often described as resisting changes in voltage.
Note: the question wording is broad, since other components (like resistors or potentiometers) are also made of conductive surfaces separated by insulating material in a mechanical sense, but the defining electrical component that specifically consists of conductive surfaces separated by an insulator and stores energy in an electric field is the capacitor.
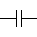
Last edited by gager797. Register to edit
Tags: none
What type of electrical component stores energy in a magnetic field?
-
Resistor
-
Capacitor
-
Correct AnswerInductor
-
Diode
There are two similar concepts often asked about: one component stores energy in an electric field, the other stores energy in a magnetic field. The component that stores energy in a magnetic field is an inductor. An inductor is typically a coil of wire.
When current flows through the coil, a magnetic field is created around it. If the coil has a ferromagnetic (ferrite or iron) core, the core becomes magnetized and the magnetic effect is stronger — this is the same principle used to make electromagnets (for example, wrapping insulated wire around a nail to magnetize it when current flows).
An inductor resists changes in current. When current is first applied it opposes the change because the magnetic field is building; once the field is established the coil behaves more like a wire. If the current is suddenly interrupted, the collapsing magnetic field induces a voltage that tries to keep the current flowing, which can produce voltage spikes or sparks. This behavior is a direct consequence of the energy stored in the magnetic field of the inductor.
Memory aids:
- Think of the word "MICE": (M)agnetic field — (I)nductor; (C)apacitor — (E)lectric field.
Last edited by rjstone. Register to edit
Tags: none
What electrical component is typically constructed as a coil of wire?
-
Transistor
-
Capacitor
-
Diode
-
Correct AnswerInductor
An inductor generally consists of a coil of wire.
The schematic symbol resembles the coil used in its construction.
The properties of an inductor depend on whether the coil surrounds a magnetic core (such as ferrite). A magnetic core increases the magnetic field produced by a given current, which increases the inductance. Wrapping insulated wire around an iron nail and applying current is the classic way to make an electromagnet — the same basic idea as an inductor or transformer.
When current through an inductor changes, the inductor resists that change by storing energy in its magnetic field. When current is turned on, the inductor initially opposes the rise in current; once the magnetic field is established, current can flow more easily. When the current is interrupted, the collapsing magnetic field attempts to keep the current flowing by inducing a voltage, which can produce a large voltage spike as the energy is released.
Last edited by rjstone. Register to edit
Tags: none
What is the function of an SPDT switch?
-
A single circuit is opened or closed
-
Two circuits are opened or closed
-
Correct AnswerA single circuit is switched between one of two other circuits
-
Two circuits are each switched between one of two other circuits
SPDT stands for Single Pole, Double Throw. It has one input (the single pole) that can be connected to one of two outputs (the double throw). In other words, a single circuit is switched between one of two other circuits. The switch connects the pole to either output; there is no third "floating" connection state.
- SP = Single Pole
- DT = Double Throw
- If the first part is SP, there is one input; if DP, there are two inputs
- If the second part is ST, there is one output for each input; if DT, there are two outputs for each input
- Common switch types: SPST, SPDT, DPST, DPDT
- Household example: a regular light switch is SPST (open/closed). A three-way light switch is SPDT, connecting the pole to one or the other of two traveler wires.
Last edited by kd7bbc. Register to edit
Tags: none

What type of switch is represented by component 3 in figure T-2?
-
Correct AnswerSingle-pole single-throw
-
Single-pole double-throw
-
Double-pole single-throw
-
Double-pole double-throw
Single-pole means that there is a single set of contacts that are connected or disconnected with the switch. Note on the diagram that there is only a single line into the switch and a single line out. Double-pole would mean that the switch could connect or disconnect two wires at once and there would be two contacts going into the switch on the diagram.
Single-throw means that there is only one "choice" for each of those contacts; with a double-throw the switch would connect the input to one of two outputs.
Memory aids:
- Triple-throw would be one of three outputs (etc.).
Last edited by kd7bbc. Register to edit
Tags: none
Which of the following battery chemistries is rechargeable?
-
Nickel-metal hydride
-
Lithium-ion
-
Lead-acid
-
Correct AnswerAll these choices are correct
All three named battery chemistries—nickel‑metal hydride (NiMH), lithium‑ion (Li-ion), and lead‑acid—are rechargeable. They are examples of secondary cells, meaning their electrochemical reactions can be reversed by applying an external current. By contrast, zinc‑carbon cells are primary batteries and are not intended to be recharged.
Memory aids:
- "Can't Zap a Carbon Zinc" (to remember zinc‑carbon batteries are not rechargeable)
Last edited by gregor. Register to edit
Tags: none
Which of the following battery chemistries is not rechargeable?
-
Nickel-cadmium
-
Correct AnswerCarbon-zinc
-
Lead-acid
-
Lithium-ion
Carbon–zinc batteries are primary cells whose chemical reactions are not readily reversible, so they cannot be effectively recharged. In contrast, nickel–cadmium, lead–acid, and lithium‑ion batteries are designed with reversible electrochemical reactions and are rechargeable (secondary) cell types.
Memory aids:
- "Can't Zap a Carbon‑Zinc" — C Z = Carbon‑zinc (can't be recharged)
- Think “primary = disposable” for carbon‑zinc cells and “secondary = rechargeable” for NiCd, lead‑acid, and Li‑ion.
Last edited by zorba. Register to edit
Tags: none
View Privacy Policy | Get help with HamStudy.org™
